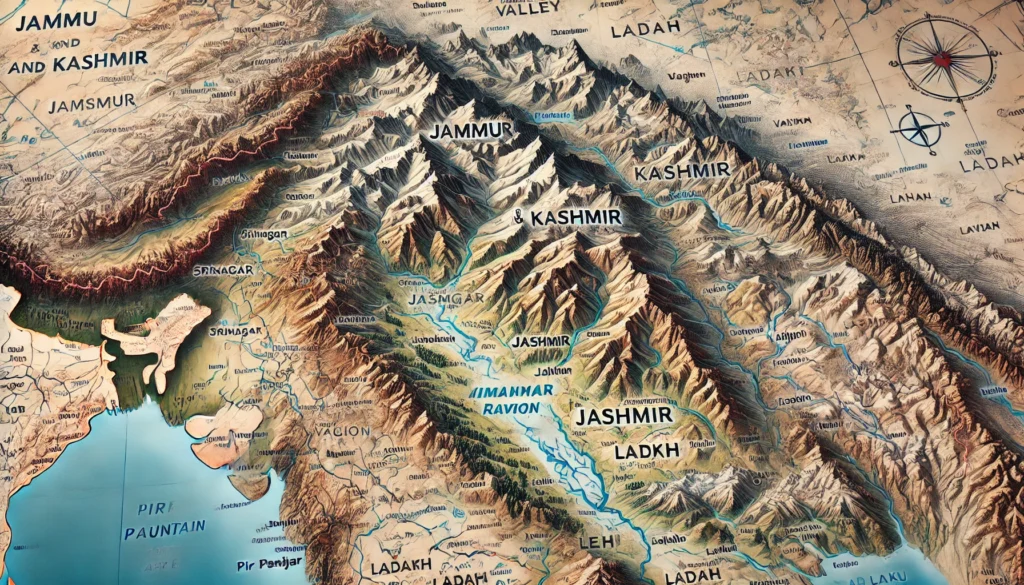
Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory of India, is renowned for its distinctive geography, culture, and history. The territory is divided into two primary regions: Jammu and Kashmir.
geographical feature
- Kashmir Valley : Situated amidst the Himalayas , this region is world famous for its beauty and natural wealth.
- Jammu : It is called the city of temples and is a confluence of hilly and plain lands.
- Ladakh (formerly part) : Until 2019 , was part of Jammu and Kashmir , but is now a separate union territory .
History and administration
- The special status of Jammu and Kashmir (Articles 370 and 35A) was removed in 2019 and it was divided into two union territories— Jammu and Kashmir And Ladakh were divided into.
- Administratively, the administrative work here is now looked after by the Lieutenant Governor under the Central Government.
Culture
- The culture here is a confluence of Hindu , Muslim , Buddhist and Sikh traditions.
- Major festivals: Eid , Diwali , Baisakhi , and Navreh.
- The local Kashmiri embroidery (sozni) , carpets , and pashmina shawls are world famous.
Tourism
- Kashmir Valley : Srinagar , Gulmarg , Pahalgam , and Sonamarg are tourist attractions.
- Jammu : Vaishno Devi temple attracts millions of devotees every year.
- Dal Lake : Experience Shikaras and Houseboats.
economy
- The main occupation is agriculture and horticulture.
- Saffron , apples , walnuts , and almonds are the major produce here.
- The tourism industry is an important part of the economy here.
Jammu and Kashmir: Extended Introduction
Jammu and Kashmir , a major union territory of India , is world famous for its natural beauty , historical importance and cultural heritage. It is called “Paradise on Earth”. The region is known for its diverse geography , traditions and rich heritage.
geographical structure
- Status and limitations
- To the north: China
- In the West: Pakistan
- To the east: Ladakh
- In the south: Himachal Pradesh and Punjab
- Total area: about 55,673 square kilometers
- Main geographical areas
- Kashmir Valley : Located in the lap of the Himalayas , it is famous for its lush green valleys , lakes , and snowy mountains.
- Jammu region : It is called the “City of Temples” , and is a centre of religious tourism.
- Karakoram Mountain Range : This region is special for its height and beauty.
History and administration
- History
- The history of Jammu and Kashmir is rich since ancient times.
- At the time of the India-Pakistan Partition in 1947 , Maharaja Hari Singh decided to include it in India.
- Special Status: It enjoyed special autonomy under Articles 370 and 35A , which were removed in August 2019 .
- Administrative divisions
- After 2019 : It will be divided into two union territories— Jammu and Kashmir And Ladakh were divided into.
- Capital :
- Summer: Srinagar
- Winter: Jammu
Culture and Tradition
- Religious diversity
- Hindus , Muslims , Sikhs , and Buddhism live here.
- Religious harmony and co-existence are the identity of this place.
- Language
- Major languages: Kashmiri , Dogri , Urdu , Hindi , and English.
- Arts and Crafts
- pashmina shawls , Kashmiri carpets , and Paper Mache These are the main crafts here.
- Sozni embroidery and wood carving are famous.
- Food & Drink
- Wazwan: Traditional Kashmiri cuisine , consisting of a variety of non-vegetarian dishes.
- Kashmiri Kahwa (tea) and Noon Chai are popular beverages.
Tourism
Jammu and Kashmir is one of the most attractive tourist destinations in India.
- Major landmarks
- Srinagar: Dal Lake , Nishat and Shalimar Bagh
- Gulmarg: Skiing and Cable Car
- Pahalgam: Trekking and Natural Beauty
- Vaishno Devi: Famous Pilgrimage Site
- Amarnath: Cave famous for the ice Shivalinga.
- Winter Sports
- Skiing and Snowboarding in Gulmarg.
economy
- Core Business
- Agriculture : Cultivation of apple , saffron , walnut , and almond.
- Horticulture : Production of world famous Kashmiri apples and saffron.
- Handicrafts : shawls , carpets , and embroidery.
- Tourism
- This state is heavily dependent on the tourism industry.
- Aquatic Resources
- Dal Lake and Jhelum River are the aquatic resources here.
Important Facts
- Special festivals
- Eid , Baisakhi , Lohri , Navreh.
- Controversy and conflict
- Historically , Jammu and Kashmir has been affected by territorial disputes and terrorism.
- After removal of Article 370 , the situation is improving.

Geographical structure
Geographical structure of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is famous for its unique geographical features. The region is located between the Himalayan mountains and is known for its high mountains , valleys , rivers , and lakes. To understand the geographical structure here, it can be divided into different parts:
1. Division of land
Jammu and Kashmir can be divided into three main geographical regions:
- Kashmir Valley
- Jammu Region
- Pir Panjal and Zanskar region
Kashmir Valley
- Location : Situated between the Himalaya and Pir Panjal mountain ranges.
- features :
- It is a crescent-shaped valley , approximately 135 kilometres long and 32 kilometres wide.
- Average altitude: 1600 m.
- Climate: The climate here is temperate. There is snowfall in winters and pleasant weather in summers.
- Major lakes: Dal Lake , Wular Lake , and Manasbal Lake.
- Major rivers: Jhelum River and its tributaries.
Jammu Region
- Location : Located in the south and is a mixture of mountainous and plain terrain.
- features :
- Altitude above sea level: 300 to 1000 metres.
- The Jammu region is also called the “City of Temples”.
- This region adjoins the Shivalik Hills and the plains of Punjab.
- The climate here is subtropical.
- Major rivers: Chenab , Tawi , and Ravi.
Pir Panjal and Zanskar region
- Location : Pir Panjal is a sub-range of the Himalayas and the Zanskar Range is situated in the upper Himalayas.
- features :
- There are high snow covered mountains here.
- The area is famous for trekking and mountaineering.
- Average altitude: 3000-4500 m.
- Life here is difficult and the population is less.
2. Mountain ranges
The landmass of Jammu and Kashmir is surrounded by several mountain ranges:
(i) Pir Panjal Mountain Range
- It forms part of the southern border of the Himalayas.
- Famous tourist places like Gulmarg and Pahalgam are located here.
- It divides the Kashmir Valley and the outer Himalayas.
(ii) Great Himalayas
- It is located to the north of the Kashmir Valley.
- The peaks here are more than 6000 meters high , like Nanga Parbat.
- This area is known for snowfall and glaciers.
(iii) Karakoram Mountain Range
- This area is situated on the border of India and China.
- The main peak here K2 ( Godwin Austin) , which is the second highest peak in the world.
- Siachen Glacier , the world’s highest battlefield , is located in this region.
3. Rivers and water resources
(i) Jhelum River
- It is considered the lifeline of the Kashmir Valley.
- This river originates from Wular Lake.
- Srinagar is situated on the banks of Jhelum.
(ii) Chenab River
- This river flows in the Jammu region and is used for power generation.
- There are several ongoing hydropower projects on the Chenab.
(iii) Ravi and Tawi rivers
- These rivers are important for agriculture and irrigation in the Jammu region.
(iv) Indus river
- It flows in the Zanskar and Karakoram region and is one of the major rivers of India.
4. Lakes and glaciers
Major lakes
- Dal Lake : Famous for houseboats and Shikaras.
- Wular Lake : India’s largest freshwater lake.
- Manasbal Lake : This lake is famous for trekking and peaceful environment.
Glacier
- Siachen Glacier : It is the highest and coldest glacier in the world.
- Kolahoi Glacier : It is the main source of the Jhelum River.
5. Flora and fauna
Vegetation
- The land here is covered with dense forests.
- Major trees: Chinar , Cedar , Pine.
- apples , walnuts and almonds are grown here.
living organisms
- Himalayan bear , Kashmir deer (hangul) , snow leopard , and monal are found here.
6. Climate
- Kashmir Valley: Temperate climate (cool summers and snowy winters).
- Jammu region: Subtropical climate (hot and humid summers).
- Pir Panjal and Zanskar: Extreme cold and snowfall.
Kashmir Valley
Kashmir Valley: A Complete Introduction
The Kashmir Valley is a major region of the Indian Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. It is called “Heaven on Earth” due to its natural beauty , rich culture , and historical importance.
geographical structure
- Location : The Kashmir Valley is situated between the Himalayas and the Pir Panjal ranges.
- Shape : It is a crescent shaped valley , the length of which is approximately 135 km and width 32 kilometers Is.
- Altitude : Average height above sea level approx. 1600 metres Is.
Main geographical features
- Mountains and hills
- The valley is surrounded by the Himalayan and Pir Panjal mountain ranges.
- The heights here remain covered with snow in winter.
- Lakes
- Dal Lake : Famous for its Shikara boats and houseboats.
- Wular Lake : It is the largest freshwater lake in India.
- Manasbal Lake : Known for trekking and serene environment.
- Rivers
- Jhelum River : The main river of the valley , which is its lifeline.
- Srinagar is situated on the banks of Jhelum.
- Glacier
- Kolahoi Glacier : It is the main source of the Jhelum River.
climate
- Summer : Pleasant weather ( 20°C to 30°C) .
- Autumn : During October-November the Chinar trees here turn red , making the valley look more beautiful.
- Winter : Extremely cold and heavy snowfall (temperature can drop to -10°C ).
- Spring : March to May , season of flowers and greenery.
Natural Beauty
is famous for its lush green valleys , snow-capped mountains , flowing rivers , and blooming gardens.
- Mughal Gardens : Nishat Bagh , Shalimar Bagh , and Chashme Shahi are the major attractions here.
- Gulmarg and Pahalgam : Green meadows , horse rides , and snowy slopes.
Cultural and social structure
- population
- The population here mainly consists of Kashmiri Muslims , Kashmiri Pandits , Sikhs , and some Buddhist communities.
- Language
- Main language: Kashmiri .
- Other languages: Urdu , Hindi , English.
- Religion and traditions
- There is religious diversity in the Kashmir Valley , but Islam is the predominant religion.
- The Sufi tradition has a deep influence here.
- Arts and Crafts
- Kashmir Valley pashmina shawls , carpets , and Paper Mache Famous for his creations.
- Festival
- Eid , Shivaratri (Herath) , Navreh , and Tulip Festival are the major festivals.
economy
- Agriculture and Horticulture
- Kashmir Valley Apples , saffron , walnuts , and Almond Is a leader in the production of.
- The saffron grown here is famous all over the world.
- Tourism
- Kashmir Valley is the main centre of tourism.
- Major places: Srinagar , Gulmarg , Pahalgam , Sonamarg.
- Dal Lake and Shikara rides attract tourists.
- Handicrafts
- Export of pashmina shawls and Kashmiri carpets is an important part of the economy here.
Importance of tourist places
- Srinagar
- Dal Lake , Nishat and Shalimar Bagh.
- The historic Jama Masjid and Shankaracharya Temple.
- Gulmarg
- Famous for skiing and cable car rides.
- Pahalgam
- Natural beauty and base camp for Amarnath Yatra.
- Sonamarg
- Famous for glaciers and trekking.
Importance and challenges
- Importance : The Kashmir Valley is a cultural and environmental treasure of India.
- Challenges :
- Political instability.
- Terrorism and security concerns.
- Climate change and environmental damage.

Jammu: Complete Introduction
Jammu Jammu and Kashmir is a major region of the Union Territory of India , known as the “City of Temples”. The region is famous for its religious sites , cultural heritage and natural beauty. Jammu is the capital of the Union Territory winter capital is also there.
geographical structure
- Location : Jammu region is located in the northwestern part of India.
- boundaries :
- Answer: Kashmir Valley
- South: Punjab
- West: Pakistan
- East: Himachal Pradesh
- Altitude : average height above sea level 300 to 1000 meters .
- Terrain :
- The area of Jammu is a mixture of flat plains and Shivalik hills.
- The region is blessed with many rivers and hills.
Main geographical features
- Mountains and hills
- Shivalik Hills : This is the lower range of the Himalayas , which surrounds the Jammu region.
- Trikuta Mountain : The famous pilgrimage site of Mata Vaishno Devi is situated here.
- Rivers
- Chenab River : It is the largest river in Jammu , important for energy production.
- Tawi River : It is considered the lifeline of Jammu.
- Ravi and Ujh Rivers : These rivers are useful for irrigation and water resources.
- climate
- Subtropical climate.
- Summers: Hot and humid.
- Winter: Cool and pleasant.
History and significance
- historical background
- The history of Jammu is rich since ancient times. Rajatarangini And it is mentioned in Mahabharata.
- this area Dogra Kings It has been the stronghold of.
- Maharaja Gulab Singh made it the capital of the Dogra Empire.
- Religious significance
- The region is famous for Hindu , Sikh , and Muslim religious sites.
- Here Mata Vaishno Devi Temple , Raghunath Temple , and Maa Baleshwar Temple Like there are holy places.
Cultural and social structure
- Population and people
- Major communities: Dogra , Pahari , Gujjar.
- The society here is a symbol of cultural diversity and harmony.
- Language
- Main languages: Dogri , Hindi , Punjabi , Urdu.
- Arts and Crafts
- Dogri paintings , wood carving , and traditional textiles are the major handicrafts here.
- music and dance
- Dogri folk songs and dances are the cultural heritage here.
- Festivals and celebrations
- Lohri : This is the main harvest festival.
- Baisakhi : It is celebrated with great enthusiasm in Jammu region.
- Navratri : At this time lakhs of devotees come to visit Mata Vaishno Devi.
Economy
- Agriculture and Horticulture
- Major crops: Wheat , Paddy , Maize.
- The climate here is suitable for gardening.
- Tourism
- Jammu is the main industry of the region.
- Every year lakhs of devotees come to visit Mata Vaishno Devi.
- Handicrafts and industry
- Dogra embroidery and shawl manufacturing.
- Carving on wood and metal.
Tourist Spots
- Religious places
- Mata Vaishno Devi Temple : It is situated on Trikuta Mountain and is one of the major pilgrimage sites of Hinduism.
- Raghunath Temple : It is dedicated to Lord Rama and is one of the largest temples in Jammu.
- Bahu Fort and Kali Temple : Place of historical and religious importance.
- Natural landmarks
- Patnitop : It is a popular hill station , famous for its lush green forests and serene atmosphere.
- Surinsar and Mansar Lake : These lakes are centres of attraction for nature lovers and tourists.
- Historical Sites
- Akhnoor Fort : Located on the banks of River Chenab , it symbolises the prosperity of the Dogra rule.
- Mubarak Mandi Palace : It was the royal residence of the Dogra kings.
Important Facts
- City of Temples : Jammu has more than 100 ancient temples.
- Trikuta Mountain : Main place of Mata Vaishno Devi.
- Tourism and Pilgrimage : Jammu is one of the major religious tourist destinations of India.
Ladakh (part in the east)
Ladakh: The Complete Introduction
Ladakh Formerly part of the state of Jammu and Kashmir , but in 2019 it was carved out as a separate Union Territories It was established as a Tibetan Buddhist monastery in 1850. It is also known as “Little Tibet” and “Land of Mountains”. Ladakh is famous for its unique geographical structure , cultural diversity , and unparalleled natural beauty.
geographical structure
- Situation
- Ladakh is located in the north of India.
- It is situated between the Himalaya and Karakoram mountain ranges.
- The region shares borders with China and Pakistan.
- Area
- Ladakh is one of the largest union territories of India.
- Its area 59,146 square kilometres Is.
- Height
- Average height above sea level: 3000 meters to 7000 meters .
- Geographical division
Ladakh can be divided into two major regions:- Leh : Mostly famous for Buddhist culture and historical monasteries.
- Kargil : Muslim-majority area , known for its historical importance and natural beauty.
Main geographical features
- Mountain ranges
- Himalaya Mountains : Southern part of Ladakh.
- Karakoram Mountains : This is the main mountain range here.
- Zanskar Mountains : This area is famous for adventure activities and trekking.
- Rivers
- Indus River : It is the main river of Ladakh and has many tributaries.
- Shyok River : It flows in the Karakoram region.
- Nubra River : It is the main river in the Nubra Valley.
- Lakes
- Pangong Tso : This is a salt water lake , part of which is also in China.
- Tso Moriri : This lake is a centre of attraction for nature lovers.
- Tso Kar : It is one of the salt lakes in Ladakh.
- climate
- Ladakh is considered one of the driest places in the world.
- are extremely cold (temperature ranges from – 30°C to – 50°C) .
History and cultural significance
- History
- In ancient times Ladakh was called the “Gateway to Tibet”.
- It was a major part of the Silk Route .
- this area Namgyal Kingdom remained under.
- Religious and cultural significance
- Ladakh is mainly a centre of Buddhism.
- There is influence of Tibetan Buddhist culture and Tibetan art here.
- The influence of Muslim culture is seen in the Kargil region.
- Language and literature
- Major languages: Ladakhi , Tibetan , Hindi , Urdu , English.
Cultural and social structure
- Religion
- Buddhism : Predominant in Leh area.
- Islam : Predominant in the Kargil area.
- Followers of Hindu and Sikh religions also reside.
- Festival
- Hemis Festival : The most famous Buddhist festival of Ladakh.
- Losar : Tibetan New Year festival.
- Dospa Festival : Festival depicting the importance of Indus River.
- Arts and Crafts
- The sculptures and paintings made in the monasteries of Ladakh are famous.
- Carving on wood and metal is also a special feature of this place.
economy
- Agriculture and animal husbandry
- , maize and mustard are cultivated in Ladakh .
- , especially yak rearing , is prominent here .
- Tourism
- Ladakh is famous for adventure tourism.
- A hub for adventure sports like trekking , biking , and mountaineering.
- Major places of visit: Leh Palace , Thikse Monastery , Shanti Stupa.
- Handicrafts
- Woolen clothes , Thangka paintings , and Tibetan shawls are the major handicrafts here.
Tourist Spots
- Leh
- Leh Palace : A masterpiece of ancient architecture.
- Shanti Stupa : This is a major Buddhist site.
- Thikse Monastery : The largest and most beautiful Buddhist monastery in Ladakh.
- Nubra Valley
- of here Double hump camel And the sand dunes are the main attraction.
- Diskit Monastery : It is the oldest Buddhist monastery in the region.
- Pangong Tso Lake
- This lake is famous for its changing colours and amazing natural beauty.
- Zanskar Valley
- This valley is known for trekking and adventure trips.
- Here Chadar Trek Famous for its performance on the frozen Zanskar River .
- Kargil
- Kargil witnessed the war of 1999 and the Kargil War Memorial here is famous.
Challenges and Prospects
- Challenges
- Difficult geographical conditions.
- Impact of climate change.
- Border tensions and security issues.
- Possibilities
- There are immense possibilities in the field of tourism and culture.
- Investment opportunities in renewable energy , especially solar energy.
History and Administration
History and Administration of Ladakh
Ladakh is a historically , culturally and strategically important region. Its history is filled with many important changes including ancient kingdoms , Tibetan influence , and as part of India in modern times.
History of Ladakh
- Ancient period
- Ancient History of Ladakh Dates back to the Kushan Empire (1st–3rd century CE) .
- This region was a place of confluence of Tibetan and Indian cultures.
- It served as a trade route between the Indus Valley and the Tibetan Plateau.
- Medieval period
- 9th century : Tibetan king took control of Ladakh. It also came to be known as “Little Tibet”.
- 10th century : Local rulers Skid Lhde started ruling Ladakh.
- Medieval era : Buddhism spread here and many monasteries were built , such as Hemis Monastery and Thikse Monastery.
- Dogra rule and British era
- 19th century : Dogra commander Zorawar Singh annexed it to Maharaja Gulab Singh’s Jammu and Kashmir state.
- 1846 : Ladakh became part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir .
- Ladakh’s strategic importance increased during the British era.
- modern history
- 1947 : At the time of India’s independence, Ladakh became a part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- 1948 : First war between India and Pakistan took place , in which part of the Karakoram region came under Indian control.
- 1962 : A large part of Aksai Chin was captured by China in the India-China War.
- 2019 : After the removal of Article 370 , Ladakh was separated from Jammu and Kashmir and made a separate union territory.
Administration of Ladakh
The administrative structure of Ladakh was reorganised after 2019 .
- Formation of Union Territory
- 31 October 2019 : Ladakh got the status of Union Territory.
- Its formation Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act , 2019 It was done under.
- Administrative divisions
Ladakh is divided into two districts:- Leh
- Kargil
- Major administrative machinery
- Lieutenant Governor ( LG) : Appointed by the Central Government.
- First Lieutenant Governor: Radha Krishna Mathur .
- Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council ( LAHDC) :
- Both the districts (Leh and Kargil) have a separate LAHDC .
- These councils have been given wide powers in local administration.
- Lieutenant Governor ( LG) : Appointed by the Central Government.
- law & Order
- The police administration of Ladakh comes under the Central Government.
- For the security of India-China and India-Pakistan borders Indian Army And ITBP ( Indo-Tibetan Border Police) is deployed.
- Judicial system
- Ladakh falls under the jurisdiction of the Jammu and Kashmir High Court.
- The cases here are heard in Srinagar and Jammu.
Challenges in the administration of Ladakh
- borderline tension
- Tension persists on the India-China (Line of Actual Control – LAC) and India-Pakistan borders.
- The Aksai Chin and Siachen areas are strategically sensitive.
- Natural and geographical challenges
- Difficult geographical conditions and climate complicate administration.
- Access to services and facilities in remote areas is a challenge.
- Local administrative authority
- The balance of powers between the Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council and the Centre is a contentious issue.
- It is necessary to establish harmony between environment and development.
- Lack of infrastructure
- health , education , and transportation facilities.
- Many areas are cut off from the rest of the country in winter.
Positive initiative
- Promotion of tourism and culture
- Several projects are underway to promote local culture and tourism.
- Adventure sports and Buddhist sites are being given prominence.
- Renewable energy
- Solar energy and wind energy are being promoted in Ladakh.
- It is India’s first Carbon Neutral Region There is a plan to make it.
- Military and infrastructure
- Military infrastructure is being rapidly developed on the borders.
- Atal Tunnel Projects like these are making transportation easier.
- Education and health
- In Ladakh Skill Development Program And health facilities are being expanded.
- Scholarships and training programmes have been started for the youth.
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir is a union territory of India , famous for its natural beauty , cultural diversity , and strategic importance. It is also called “Heaven on Earth”. In 2019 , the special status of Jammu and Kashmir was abolished and it was divided into two union territories: Jammu and Kashmir And Ladakh .
geographical structure
- Location and area
- It is located in the north-western part of India.
- The area of Jammu and Kashmir is approximately 55,673 square kilometres Is.
- boundaries
- In the north and north-west: Pakistan-occupied Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan.
- To the east: Ladakh and China.
- In the south: Himachal Pradesh and Punjab.
- Natural features
- There are three key areas here:
- Jammu region : It is a mixture of plain and hilly areas.
- Kashmir Valley : It is a lush green valley surrounded by the Himalayas.
- Poonch and Rajouri : An area with high mountain peaks and beautiful valleys.
- There are three key areas here:
- climate
- Jammu has a subtropical climate.
- The Kashmir Valley experiences cold and snowy winters.
History
- Ancient period
- Mention of Jammu and Kashmir in ancient texts Mahabharata And Nilamata Purana It is available in.
- Kashmir is called the land of sage Kashyap.
- Medieval period
- in Kashmir in the 14th century shah mir Islam spread under his leadership.
- The region also remained under the Mughals and was annexed by Akbar in 1586 .
- Dogra rule ( 1846–1947)
- Amritsar Treaty Under Maharaja Gulab Singh purchased the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir from the British East India Company.
- The Dogra dynasty ruled until 1947 .
- modern history
- 1947 : At the time of India’s independence, Maharaja Hari Singh of Jammu and Kashmir merged it with India.
- 1948 : Following the Indo-Pakistani War , a part of the region came under the control of Pakistan (Pakistan-occupied Kashmir).
- 1954 : Jammu and Kashmir got special status (Article 370) in the Constitution of India.
- 2019 : Articles 370 and 35A were repealed and Jammu and Kashmir was made a Union Territory.
administrative structure
- Formation of Union Territory
- 31 October 2019 , Jammu and Kashmir was given the status of a Union Territory.
- Here is a Assembly Is.
- Major administrative units
- 22 Districts : The major districts among these are Jammu , Srinagar , Pulwama , Anantnag , Baramulla , and Udhampur.
- Capital:
- In summer : Srinagar.
- In winter : Jammu.
- Major administrative machinery
- Lieutenant Governor ( LG) : Appointed by the Central Government.
- Assembly : Laws are made through elected representatives.
- Judicial system
- There is a separate High Court for Jammu and Kashmir.
Cultural and social structure
- Religious diversity
- Muslim majority state (Kashmir Valley).
- Hindu majority in Jammu region.
- There are also followers of Sikhism and Buddhism.
- Language and literature
- Major languages: Kashmiri , Dogri , Urdu , Hindi , and English.
- Poetry and music have a special place in the Kashmir Valley.
- Arts and Handicrafts
- Kashmir’s carpets , pashmina shawls , and wood carvings are world famous.
- Kashmiri Sufi music and folk dances of the Dogra culture are popular.
- Festival
- Eid , Shivratri (Herath) , Baisakhi , and Nauhriz are the major festivals here.
economic structure
- Agriculture and Horticulture
- Main crops: Paddy , Maize , Barley , and Wheat.
- Saffron , apples , and walnuts are the major products here.
- Tourism
- Tourism is the mainstay of the economy here.
- Major destinations: Srinagar , Dal Lake , Gulmarg , Pahalgam , and Vaishno Devi.
- Handicrafts and Carpet Industry
- Kashmir’s carpets , pashmina , and paper-machine products are famous.
- Energy and industry
- Hydroelectric projects (e.g. , Baglihar and Salal).
Major tourist spots
- Kashmir Valley
- Dal Lake : Famous for houseboats and Shikaras.
- Gulmarg : Famous for skiing and ropeway.
- Pahalgam : Main route for Amarnath Yatra.
- Jammu Region
- Vaishno Devi : Major pilgrimage site of Hindu religion.
- Patnitop : Hill Station.
- Other landmarks
- Sonamarg : Famous for trekking and adventure sports.
- Mughal Gardens : Gardens laid out in the traditional Persian style.
Challenges and Prospects
- Challenges
- Border Tension : Clashes and Infiltration along the India-Pakistan Border.
- Terrorism : Establishing peace in the valley.
- Natural disasters : Landslides and floods.
- Possibilities
- Tourism : Potential to develop it as “Paradise on Earth”.
- Agriculture and Horticulture : Export of saffron and apples.
- Energy generation : Expansion of hydropower projects.
Article 370 and 35A
Introduction to Article 370 and 35A
Article 370 and 35A There were special provisions in the Indian Constitution , which gave Jammu and Kashmir a separate status and special autonomy. Due to these provisions, Jammu and Kashmir had special rights compared to other Indian states.
5 August 2019 On 20 November 2014 , the Government of India abolished these articles and converted Jammu and Kashmir into a union territory.
Article 370
Article 370 It was part of the Indian Constitution , which provided special autonomy to Jammu and Kashmir. It was approved by the Constituent Assembly in 1949 and came into force on 26 January 1950 .
Key Features
- Special status
- Jammu and Kashmir was given special autonomy in the Indian Constitution compared to other states.
- could legislate on Jammu and Kashmir only in three subjects (foreign affairs , defence , and communications).
- Separate constitution
- Jammu and Kashmir had its own constitution , which came into force on 17 November 1956 .
- Limitations in law making
- The orders of the President of India or the laws of the Parliament could be implemented in Jammu and Kashmir only if the state government consented .
- Separate flag and rights
- Jammu and Kashmir had its own flag and emblem.
- An emergency declared by the President of India could not be imposed in the state (except a national emergency).
Article 35A
Article 35A was added to the Indian Constitution through a Presidential order in 1954. It provided special rights to the permanent residents of Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Features
- permanent resident status
- Only permanent residents had the right to purchase land , hold government jobs, and receive other privileges.
- Impact on women’s rights
- If a woman from Jammu and Kashmir got married outside the state , she and her children would not get permanent resident status.
- Economic and social impact
- People from outside the state did not have the right to buy property here or get government jobs.
Abrogation of Article 370 and 35A
On 5 August 2019 , the Government of India abolished Articles 370 and 35A .
Key Decisions
- Article 370 were removed
- It was abolished through a Presidential order and a resolution passed by Parliament.
- The special status of Jammu and Kashmir was abolished.
- Reorganisation of Jammu and Kashmir
- Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two union territories:
- Jammu and Kashmir ( with assembly).
- Ladakh ( without Assembly).
- Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two union territories:
- full implementation of the Indian Constitution
- All articles of the Indian Constitution are now applicable in Jammu and Kashmir.
Effects of cancellation
Positive effects
- National Unity
- Jammu and Kashmir now has the same rights as other states of India.
- strengthens the goal of “Ek Bharat , Shreshtha Bharat”.
- Growth prospects
- External investment and new employment opportunities increased.
- Land and resources can be used more efficiently.
- social equality
- Women and Dalits got equal rights.
- Now all Indian citizens can buy land and do business in the state.
Challenges
- safety issue
- There was a possibility of increased terrorism and protests following the cancellation.
- The deployment of security forces increased.
- Political instability
- Local political parties opposed the decision.
- Regional discontent grew.
- International response
- Pakistan and China criticized the decision.
- International attention to the Kashmir issue increased.

Ladakh
Introduction to Ladakh
Ladakh It is a union territory of India , known for its natural beauty , Buddhist culture , and strategic importance. It is also called “Little Tibet” and “Roof of the World”. After the reorganization of the state of Jammu and Kashmir on 31 October 2019 , Ladakh was given the status of a separate union territory.
geographical structure
- Location and area
- Ladakh is located in the northern part of India.
- Its area is approximately 59,146 square kilometres Is.
- boundaries
- In the north: China’s Xinjiang province.
- In the east: Aksai Chin (currently occupied by China).
- In the west: Jammu and Kashmir.
- In the south: Himachal Pradesh.
- Natural features
- Karakoram and Himalaya mountain ranges The major structures of Ladakh are:
- The world’s highest roads and passes are located here , such as Khardung La pass .
- Major rivers: Indus , Zanskar , and Shyok.
- climate
- The climate of Ladakh is cold and dry.
- In summers here it is mildly hot during the day and bitterly cold at night.
History
- Ancient period
- was part of the trade route between Tibet , Central Asia and India.
- This region was a major center of Buddhism and Buddhist culture.
- Medieval history
- Ladakh was ruled by Buddhist rulers from the 9th century onwards.
- the 17th century it was included in the Dogra rule of Jammu.
- modern history
- After India’s independence in 1947 , Ladakh became a part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- 1962 , part of Aksai Chin came under Chinese control.
- 2019 , it was given the status of a separate union territory.
administrative structure
- Formation of Union Territory
- 31 October 2019 , Ladakh was declared a Union Territory.
- There is no Legislative Assembly in Ladakh.
- Major districts
- There are two districts in Ladakh:
- Leh : It is the administrative headquarters of Ladakh.
- Kargil : It is a Muslim majority area and has historical importance.
- There are two districts in Ladakh:
- Administrative machinery
- Lieutenant Governor ( LG) : Appointed by the Central Government.
- LAHDC ( Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council) : Separate councils for Leh and Kargil.
Cultural characteristics
- Religion and society
- Buddhism is predominant , especially in the Leh area.
- Shia Muslim community is in majority in Kargil.
- Language
- Ladakhi (Bhoti) , Hindi , Urdu , and English are the major languages.
- Traditions and festivals
- Hemis Festival : The biggest Buddhist festival in Ladakh.
- Ladakhi New Year (Losar) .
- Durga Puja and Eid Celebrated in Kargil.
- Arts and Handicrafts
- Tantric paintings (Thangka paintings) are famous in the Buddhist monasteries here.
- Wood carvings and handmade woolen clothes are also the identity of this place.
Natural and environmental features
- Tourist Spots
- Pangong Lake : This is the most famous tourist destination in Ladakh.
- Nubra Valley : Double hump camel safari takes place here.
- Monasteries and stupas : Hemis , Thiksey , and Shanti Stupa.
- Zanskar Valley : Famous for trekking and adventure sports.
- Wildlife
- Snow leopard , Tibetan wild ass , and reindeer are found here.
- Hemis National Park It is world famous.
- Natural problems
- Climate change and melting of glaciers.
- Water scarcity in cold desert region.
economic structure
- Agriculture
- Major crops: Barley , wheat , and peas.
- Cool weather vegetables and fruits like apples and apricots are produced.
- Tourism Industry
- Trekking , mountaineering , and motorbike excursions are popular.
- The tourist places here are famous in India and abroad.
- Industry and energy
- Handicrafts and woolen textile industries are important in Ladakh.
- Hydropower projects and the region’s potential for solar energy.
Strategic importance
- India-China border dispute
- There is an India-China border dispute in the Aksai Chin region.
- 2020 conflict in the Galwan Valley underlines the strategic importance of the region.
- Karakoram and Siachen Glacier
- This is the highest battlefield in the world.
- The Indian Army is deployed here.
- Indus River
- This region is important for India’s water security.
Challenges and Prospects
- Challenges
- Harsh climate and snowfall.
- Lack of infrastructure and health services.
- Borderline stress and security.
- Possibilities
- Huge potential for tourism and adventure sports.
- Development in the field of solar and wind energy.
- Expansion of cultural and religious tourism.

Culture
Detailed introduction to the culture of Ladakh
Ladakh , also known as “Little Tibet” , is a culturally rich and diverse region located in the northern border region of India. Its culture is a mixture of Buddhism , Tibetan traditions , and Islam. The culture of Ladakh is significantly influenced by the historical , religious , and geographical ties between India and Tibet .
Religion and beliefs
- Buddhism
- The most prominent part of Ladakh’s culture Buddhism , which is deeply rooted in the society here.
- Most of the people of Ladakh tibetan buddhist And this region has been a major center of Buddhism.
- There are many monasteries (Gompa) here , such as Hemis , Thiksey , Lhamo Yur , and Monastery The ancient traditions of Tibetan Buddhism are alive in.
- Buddhist followers in Ladakh the dalai lama They also give great respect to him.
- Ladakhi Architecture : The architectural style of Buddhist monasteries is an important part of the culture here. The paintings on the walls and tantric paintings (thanka) are also special in these monasteries.
- Islam
- Kargil And in some other areas the Muslim community is in majority.
- The Muslim community is mainly Shia Muslims , and distinct Shia Islamic traditions are prevalent in the Kargil area.
- Ramadan , Eid , and Muharram are among the major Islamic festivals here.
- Islamic Architecture : Mosques and madrassas in Kargil and other Muslim-dominated areas reflect Islamic culture.
- Hinduism
- The influence of Hinduism is also seen in some parts , especially in himalayan mountains Near , where gods and goddesses are worshipped.
- Vaishno Devi Followers of also organize religious festivals at some places in Ladakh.
Languages and literature
- Ladakhi (Bhoti)
- Ladakhi language , which Bhoti It is a major language of the family , it is the main language here. It is quite similar to the Tibetan language.
- There are many words in Ladakhi folktales , poems , and Poets ‘s works are popular.
- The literature here is mainly based on religious texts , history and folklore.
- Hindi and Urdu
- Hindi and Urdu are also widely spoken , especially in urban areas.
- Urdu’s influence is mainly on the Muslim community.
- English
- The English language is also used for education and administration.
Festivals and observances
- Hemis Festival
- This is the biggest and most famous Buddhist festival of Ladakh , which Hemis Monastery It is celebrated in.
- This festival is dedicated to the prominent ascetics and the dalai lama It is celebrated with worship and prayers.
- This festival features traditional dance , music , and the wearing of colourful costumes.
- Losar (Ladakhi New Year)
- In Ladakh Losar ( Ladhaki New Year) festival is traditionally celebrated according to the Buddhist calendar.
- This festival is an opportunity for families to gather and follow traditions.
- Eid
- Eid And Ramadan are celebrated with great pomp by the Muslim community , especially Kargil In.
- Fasts are observed during Ramadan and massive congregational prayers are offered on the day of Eid.
- Diwali
- by the Hindu community Diwali It is also celebrated , in which lamps are lit and happiness is shared with family members.
Arts and Handicrafts
- thanga painting
- Thanka A painting style associated with Tibetan Buddhism , prevalent in the monasteries and shrines of Ladakh.
- This painting is traditionally used to depict Buddhist deities and religious paintings.
- Buddhist Architecture
- The architectural style of the monasteries of Ladakh is unique. These monasteries include paintings on the walls , beautiful statues , and Buddhist tantras.
- giant buddha statues And domes of temples are a major part of Ladakhi architecture.
- Handicrafts
- In Ladakh traditional woolen clothing , pashmina shawls , and Handmade Carpets Are famous.
- create wood carvings , silver jewellery , and copper utensils.
Traditional clothing and dress
- Ladakhi Dress
- men and women traditional Cho They wear a kada , which is a kind of long woollen garment.
- Cho is usually worn in winter , as it is very warm.
- traditional women’s clothing head wrap And Bangles Are included.
- Traditional jewelry
- special types of women Silver jewelry , which is part of their cultural identity .
Cultural Traditions and Folk Art
- Folk dance and music
- Traditional Indian cuisine in Ladakh Folk Dance And music has a special place.
- Ladakhi Folk Songs And dance Occur on special occasions , such as weddings , festivals and religious events.
- Daman And Dole As musical instruments are used.
Preservation of culture and challenges
- Preservation of culture
- Ladakh’s traditional culture , religion and art remains a priority , especially through Buddhist monasteries and shrines.
- The traditions and art here are preserved and promoted by the local communities.
- Challenges
- Traditional culture also faces crisis due to modernity and external influences.
- The increasing impact of tourism is increasing the possibility of change in culture.
Tourism
Detailed Introduction to Ladakh Tourism
Ladakh , also known as the “Roof of the World” , is a unique and exciting tourist destination located in the northern border region of India. With its snow-capped peaks , cold and dry climate , rugged mountain ranges , and tranquil lakes, it has become a major destination among tourists. It has a unique blend of Buddhist monasteries , ancient forts , and adventure sports , making it attractive for every type of tourist.
Major tourist spots
- Leh and surrounding areas
- Leh : The main city and administrative center of Ladakh. Its Buddhist monasteries , markets , and historical sites attract tourists.
- Shanti Stupa : It is a white marble stupa , situated high above the city. This place is famous for peace and meditation and offers a beautiful view of the city from here.
- Leh Palace : This is an ancient palace , which was the residence of Ladakhi kings. From here one can see the beautiful valleys and hills of Ladakh.
- Pangong Lake
- Pangong Lake The most famous tourist destination of Ladakh is this lake. This lake is situated at an altitude of 14,000 feet above sea level and is near the border of India and China.
- This lake is famous for its beautiful blue waters and surrounding mountain views. Camping and boat ride facilities are also available on the lake shore.
- The lake is significant not only for its spectacular natural beauty but also for being a scene from the movie “3 Idiots”.
- Nubra Valley
- Nubra Valley It is about 150 kilometers away from Leh and this place is known as a cold desert.
- The major attractions here Khardung La Pass ( the world’s highest motorable pass) , double-humped camels (Bactrian camels) , and the Nubra River.
- The area also offers Buddhist monasteries and beautiful surroundings along with trekking and adventure sports facilities.
- Zanskar Valley
- Zanskar Valley Ladakh is a very beautiful and peaceful place. It is surrounded by winding paths and high mountains.
- The major attractions here Pahung Monastery has a beautiful view of the monastery and the Zanskar river . This place is ideal for trekking and nature lovers.
- Hemis Monastery and Hemis Festival
- Hemis Monastery It is the largest and most famous Buddhist monastery in Ladakh. This monastery dates back to the 17th century and followers of Buddhism perform religious activities here.
- Hemis Festival It is the biggest religious and cultural festival in the city , showcasing dance , music , and other traditions of Buddhism . This festival is celebrated in July and is a major attraction for tourists.
- Siachen Glacier
- Siachen Glacier It is called “the world’s highest battlefield”. This glacier is an adventure spot where the Indian Army is stationed.
- Even though it is a military area , trekking and adventure activities can be done near here.
- Khardung La Pass
- Khardung La The pass is famous as the highest motorable pass in Ladakh , situated at an altitude of around 18,380 feet.
- The place is ideal for adventure lovers and offers views of the most beautiful valleys and mountain ranges of Ladakh.
- Torlegg and the monastery
- Torleg It is a small village which has places ideal for trekking.
- The monastery here , Matho Monastery , is a historical site where traditional Tibetan Buddhist paintings can be seen .
adventure tourism
- Trekking and Hiking
- Ladakh is a major Trekking and Hiking The hilly trails , valleys , and alpine forests here are ideal for adventure tourism.
- Some of the major trekking routes are: Marsimik La , Zoskar Valley Track , and Drass Valley Trek Are included.
- Mountain biking
- In Ladakh Mountain biking Facilities of biking are also available. The experience of biking on the high passes and desert roads here is extremely thrilling.
- Leh to Nubra Valley , Kargil to Zanskar Valley The trails are famous for mountain biking.
- River rafting
- In Ladakh River rafting can also be experienced. Here Indus River And Zanskar River It is famous for rafting. It is an adventurous and thrilling activity which takes you along the beautiful scenery of the river bank . Presents it.
- Skiing and Snowboarding
- winter season in ladakh Skiing and Snowboarding Like adventure sports are also played.
- Nimu and Pangong Lake One can have a good skiing experience in the area.
Arts , Culture and Festivals
- Local arts and handicrafts
- Ladakhi Handicrafts And Art Very popular among tourists. Handmade woollen clothes , pashmina shawls , and Tibetan art sculptures are special attractions here.
- of here Thangka Painting And tibetan buddhist religious painting It is famous among the tourists.
- Festival
- Losar ( Ladakhin New Year) and Hemis Festival These are the major festivals here.
- , dance , and religious events during these festivals provide a unique experience for tourists.
Natural beauty and wildlife
- Natural Beauty
- Despite the lack of greenery in Ladakh , its desert landscape and snow-capped mountain views are extremely attractive.
- of here lakes , glaciers , and high mountains Provides natural peace and beauty to the tourists.
- Wildlife
- In Ladakh Snow leopard , reindeer , Tibetan wild ass , and Hummingbirds Rare species of are found.
- Hemis National Park And Tso Kar The area is an ideal destination for wildlife lovers.
Modes of entry and travel
- air route
- Main airport of Ladakh Leh airport , which is connected to major Indian cities.
- Regular flights are available from Delhi , Srinagar , and other major cities.
- Road
- Ladakh is also accessible by road. Leh-Manali Highway And Leh-Srinagar Highway There are major road routes.
- Khardung La Pass And Rohtang Pass Like high passes are the attractions during road trip.

Economy
Detailed introduction of the economy of Ladakh
Ladakh , located in a very remote and high-altitude region of India , exhibits a unique and distinctive economy. The economy depends mainly on agriculture , tourism , commerce , and government services. Despite this , its conditions and resource limitations make it a developing region. The characteristics of Ladakh’s economy are different from others , due to its geographical and cultural environment .
1. Tourism industry
in Ladakh’s economy Tourism The most prominent region is Ladakh. Its snow-capped peaks , beautiful lakes , Buddhist monasteries , and adventure tourism attractions make Ladakh a major tourist destination.
- Income from tourism
- Tourism boosts local business , hoteliers , transportation services , and sales of handicraft products.
- The increasing number of tourists in Ladakh is helping the locals to earn income especially through homestays and guesthouses.
- Major tourist activities , such as trekking , river rafting , mountain biking , and skiing , drive Ladakh’s tourism industry.
- Agriculture and animal husbandry
are an important part of Ladakh’s economy Agriculture and animal husbandry Although the environment here is not suitable for agriculture .- Agriculture : Ladakh mainly produces Wheat , barley , maize , and vegetables are grown , but there are limitations to cultivation due to the altitude of the land and the climate.
- Animal Husbandry : People here Animal Husbandry do , especially yak , goat , and lamb They raise them. They feed on yak milk. Cheese And Ghee Is made.
- Fruits and nuts : Some places in Ladakh apples , walnuts , and Jamun Such as fruits are grown , which contribute to the local economy.
3. Handicrafts and cottage industries
In Ladakh Handicrafts And Cottage Industry has a major contribution. The people here sell their traditional arts , crafts and products locally and nationally.
- textile industry :
- pashmina shawls , woollen clothes , and thanga painting Ladakh has famous handicrafts. These products are popular among tourists and are a major source of income.
- Traditional Ladakhi Clothing And head wraps There are also handicraft products here.
- Ladakhi Jewellery :
- Ladakh’s traditional silver and copper jewelry These are part of the cultural heritage here. These ornaments are also a centre of attraction for tourists.
4. Government services and employment
in Ladakh’s economy government sector also has a significant contribution. This region is very important from the national security and administrative point of view as it is located in the border areas of India.
- Government Services
- Central and state government in Ladakh Services And the administrative presence is strong. Indian Army And Border Security Force ( BSF) has an important place here.
- Various government schemes , such as health , education , and infrastructure development , help to strengthen the local economy.
- employment
- Government organizations such as Leh and Kargil Municipal Corporation , Ladakh Tourism Department , and Ladakh Education Board Provides employment opportunities in.
- Apart from this , various government schemes also provide training and skill development opportunities to the local people.
5. Commerce and trade
Ladakh’s commercial activities are mainly limited to small businesses , traders and markets. Trade here is on a large scale border trade And Local products is based on sales of.
- border trade
- Ladakh trade tibet And China Historically, this trade is associated with the Indian market. But at present, this trade is mainly Traditional trading And Smuggling It happens in the form of.
- From Ladakh Nubra Valley , Leh And Kargil Traditional trade is prevalent in areas such as.
- local market
- Leh Bazaar And Kargil Bazaar It is the main commercial center of Ladakh. Handicrafts , Buddhist religious products , clothes , and other goods are sold here .
- Wholesaler And Shopkeeper In addition to local products, food items , tools , and other essential goods are also sold.
6. Energy and mineral resources
Ladakh has limited access to energy supplies and mineral resources , but the region is still full of potential in the future.
- energy
- Solar Energy And hydropower Such renewable energy sources have a very high potential in Ladakh.
- Because of the climate and environment , solar power projects are particularly important in Ladakh. The government has Solar Energy Many schemes have been made to promote the projects.
- Mineral Resources
- Ladakh has limited reserves of minerals , but still Lithium And Iron Like there is possibility of mineral deposits.
- in some parts of Ladakh Petroleum And natural gas There are reports of possible reserves of , but their survey is still ongoing.
7. Challenges and direction of development
Ladakh’s economy faces many challenges. These include geographical distance , climate change , and Limitations of resources Are prominent.
- Geographic and climatic challenges
- Ladakh’s harsh climate and high altitude pose a major challenge to the development of agriculture and other industries.
- Apart from this , climate change may have a negative impact on traditional farming here.
- Direction of development
- modern technological advances , the growth of tourism , and Use of renewable energy sources These could be steps in a positive direction for the economy of Ladakh.
- Smart city development , modern infrastructure And Expansion of local business Such steps can boost economic growth in the region.
Kashmir Valley
Kashmir Valley Jammu and Kashmir is a major and historical region of the state , known for its natural beauty , rich cultural heritage and historical importance. This valley is located in the foothills of the Himalayan Mountains and is located in the north of India. The area of Kashmir Valley is about 55,538 square kilometers and it is one of the main geographical and cultural centers of Jammu and Kashmir.
Geographical location and structure
- Geographical location :
The Kashmir Valley is located in northern India , and is situated between the Himalayan mountain ranges. This valley is one of the highest mountain regions of the Indian subcontinent. Kashmir Valley , Pakistan Occupied Kashmir ( PoK) controlled by Pakistan in the west while it is surrounded by Himachal Pradesh to the east And Ladakh The main water flow of this valley is Jehamuk River ( Jehamuk River and other tributaries). - Climate :
The Kashmir valley has a pleasant and moderate climate with snowfall in winters and cold winds in summers. The cold climate leads to snowfall here , which is important for tourism and agriculture. - Land Use :
The land of the valley is primarily agricultural and has Fruit production ( apple , walnut , grapes , etc.) and vegetables are important agricultural products. Here Tea Plantation are also famous.
History of Kashmir Valley
The Kashmir valley has a very old historical significance and its history is a mixture of various cultures and empires.
- Ancient History :
Kashmir valley is mentioned in ancient Hindu and Buddhist texts. Kashmir is called Hinduism And Buddhism It was considered a major center of. The Kashmiri royal dynasty ruled here , and the cultural contribution of the Kashmiri Pandits here was huge. There were also followers of Buddhism in Kashmir , and the people here Afghan Rulers And Mughal Empire The region was ruled by. - Mughal Era :
Mughal Emperor Akbar During his time, the Kashmir valley was seen as an important and beautiful region. He rebuilt the gardens and tourist places here and made Kashmir a major horticultural center. The famous Mughal gardens and Dal Lake It was developed during the time of Akbar. - Modern History : After the partition of India in
1947 , the future of the Kashmir Valley became uncertain. Most of Kashmir joined India , but Pakistan occupied some parts of the region , which is today Pakistan . Pakistan Occupied Kashmir ( PoK) Since then, there has been a situation of political instability and conflict in the Kashmir Valley.
Culture and language
- Culture :
The culture of the Kashmir Valley is a mixed and diverse culture with influences of Hindu , Muslim , Buddhist and Sikh cultures. Culture of Kashmiri Pandits , Sufi traditions , and Cultural heritage of Kashmiri Muslims They are an important part of the life and art of the valley. Kashmiri crafts ( especially Kashmiri embroidery , shawls and carpets) and Kashmiri Music and Dance are extremely famous. - Language :
Main language in Kashmir Valley Kashmiri , which is influenced by Dogri and Punjabi languages. Apart from this , there is Urdu is also widely spoken , especially among the Muslim community. Punjabi , Hindi , and English is also used as a second language. - Religious diversity :
The Kashmir Valley has historically been Hinduism And Buddhism It has been the center of but at present the Muslim community is dominant here . Srinagar located in Original Guru Dattatreya Temple And Shankaracharya Temple such as Hindu religious places , and Cleric Monastery Like Muslim religious places reflect the cultural heritage here.
Economic Activities
The economy of the Kashmir Valley is mainly based on agriculture , handicrafts , and tourism.
- Agriculture :
Cultivation is mainly done on the fertile land of the valley apples , walnuts , pistachios , and Rice are grown. Here Kashmiri Shawl And Kashmiri Embroidery are also major products. Kashmiri horticulture and agriculture is very important , and Kashmir’s Apple Production It is famous all over the world. - Handicrafts :
Kashmir embroidery , Kashmiri shawls , carpets , and rug are very famous. These handicraft products are in demand all over the world. Apart from this Cashmere Quilt And Kashmiri embroidered fabric are also mainly exported. - Tourism :
The tourism sector of Kashmir valley is very big and beautiful places like Dal Lake , Gulmarg , Pahalgam , and Sonamarg These are tourist attractions. Here in winters skiing , and in the summer Tracking And Picnic Tourists come here for Kashmir. The weather , snowfall and natural beauty of Kashmir make it one of the major tourist destinations in the world.
Problems and challenges
A major problem in the Kashmir Valley Political instability And Terrorist activities Since 1947 , there has been a conflict between India and Pakistan over the future of Kashmir , resulting in several wars and conflicts in the valley. In addition , political disagreements and the activities of separatists in the region also affect economic development.
Terrorist violence And safety issue There are major obstacles in the way of development in this area. Apart from this , climate change And Water shortage Environmental issues such as these also remain a challenge for the sector.
Jammu
Jammu Jammu and Kashmir is a major and historical region of the state , which is mainly famous for its religious importance , cultural heritage and geographical diversity. This region is located in the northwestern part of India and Jammu and Kashmir State Of Southern parts Jammu has an area of about 22,000 square kilometers and it is the largest city in the state of Jammu and Kashmir. Summer capital It is also famous as.
Geographical location and structure
- Geographical Location :
Jammu is situated to the south of the Kashmir valley and it Punjab , Himachal Pradesh , and Pakistan’s Punjab Province It shares borders with Jammu region to the west Rajouri And Poonch Districts , formerly Udhampur And Kathua districts. Jammu has historical and geographical importance, especially its military strategic position And Commercial Routes It is because of. - Climate :
The weather of Jammu is generally hot in summers and cold in winters. The temperature in summers can reach 35°C , while in winters the temperature can fall to -2 °C due to snowfall . Monsoon is also a major meteorological phenomenon which affects the agriculture of the region . - Geographical Diversity :
Various geographical formations are found in the Jammu region , including Mandher Mountain And Shivalik Hills The major ones are the valleys and rivers of Jammu , such as The Tawi River further enhances the natural beauty of this area .
History
- Ancient History :
The history of Jammu is linked to ancient times , and this region has been inhabited by various Hindu Dynasties And Muslim Empires Jammu has been a part of the ” Jambu “ It was known as Jammu. Jammu is mentioned in the Mahabharata and other ancient texts. - Mughal period :
Jammu region was an important place during the reign of the Mughals. Mughal emperors Akbar Horticulture and water management improved in Jammu during this period. Famous temples of Jammu Orchards And Palaces It was constructed during this period. - Freedom Struggle :
The state of Jammu and Kashmir had a special contribution in the Indian freedom struggle. The people here were involved in various movements against the British rule , and Jammu mehboob shah And other leaders fought against British rule. - Current Status : Jammu and Kashmir became part of the state after the partition of India in
1947. After the Pakistani invasion of the Kashmir Valley , Jammu became part of India. In Jammu There is a long border with Pakistan controlled territory (POK) . Presently Jammu region is important for India from military and political point of view.
Culture and language
- Culture :
The culture of Jammu is a mixture of Indian traditions , including Hinduism is prominent , but here Muslims , Sikhs , and other religious communities also contribute. Major cultural festivals of Jammu region maha shivaratri is , while Vaishno Devi Temple and baba amarnath The visit is also important from religious point of view. - Language :
Mainly in Jammu Kashmiri , Hindi , and Urdu is spoken. The linguistic diversity and cultural richness here is reflected in the folk songs , dances and traditions of the region. - Religious diversity :
Hinduism is the predominant religion in Jammu , but here Sikhs , Muslims , and Christian communities also live. Vaishno Devi Temple , Baba Amarnath And Raghunath Temple Religious places like these are important attractions here. In Jammu Gurdwaras And Mosques can also be seen , which reflect the religious diversity here.
Economic Activities
- Agriculture :
The economy of Jammu mainly depends on agriculture. Here Rice , wheat , fruits , and vegetables Are grown. apples , walnuts , and Grape Like fruits are the major agricultural products of Jammu. Tobacco , Kashmir shawls , and other handicrafts are also major products here. - Handicrafts :
The handicraft sector of Jammu is also especially famous. Here Kashmiri embroidery , carpets , and Leather Products They are special. shawl , quilt And Kashmiri Handicrafts The major export products of Jammu are. - Tourism :
Jammu has a very flourishing tourism industry. Major tourist destinations such as Vaishno Devi Temple , Raghunath Temple , Shivkhori , Baba Amarnath Yatra , and area These are the main attractions here. area And Udhampur Places like these are major centers of religious and adventure tourism. In Jammu winter And Heat Tourists come in both seasons , especially in winter Snow Tourism and in the summer Religious travel For.
Problems and challenges
- Security situation :
The security situation in Jammu region is complex because it India-Pakistan border It is located near. Here Terrorist activities and at the border Military conflict There remains a possibility of a terrorist attack. For these reasons, the security situation in this region is always sensitive. - Terrorist activities :
Social and economic activities have been affected due to terrorism in some parts of Jammu and Kashmir. The region has been the target of terrorists and separatist forces , which has adversely affected the life of the people.
Lack of development :
The pace of development is slow in some areas of Jammu region. There is a need to improve water , electricity , education and health services so that the lifestyle of the common people here can be improved.
Dal Lake
Dal Lake is the most famous and historical lake of Kashmir valley , which Srinagar Located near the city. This lake is considered a symbol of the natural beauty of Kashmir and is called ” Jewel of Kashmir” It is also called Dal Lake. Dal Lake is not only the center of Kashmir’s tourist destination , but it also holds an important place in the cultural and historical importance of Kashmir.
Geographical location and structure
- Location and size :
Dal Lake is located to the northwest of Srinagar city and Himalaya It is one of the major lakes of Kashmir valley, located in the foothills of the Himalayas. The size of the lake is approximately 22 square kilometers and its length is approximately 7 Kilometers and width approx. 3 Kilometers Its depth is somewhere 5 meters can happen till - Climate and weather :
The weather of Dal Lake is cool and pleasant like other parts of Kashmir valley. During snowfall in winters, this lake freezes completely , while in summers its water is clear and calm. - Water source :
Dal lake water is mainly rivers and streams And sources of water comes from. In this lake Jhelum River The water of the lake also enters the pond , which gives it renewal. On the shores of the lake Vegetation And Lotus flowers are also found.
History and cultural significance
- Historical importance since ancient times :
Dal Lake is mentioned in ancient Kashmiri literature and history. King Yudhishthira And Mughal Emperors In the times of the Mughals, it was considered as a major reservoir and an attractive place. The Mughals built beautiful palaces on the banks of this lake. Mughal Gardens and Artificial Island Had made it. - Mughal Emperor Akbar and Kashmir :
Mughal Emperor Akbar Dal Lake was rebuilt and beautified by him. He was very impressed by the beauty of Kashmir and built gardens and orchards on the banks of Dal Lake. Boats ( Shikaras) and The concept of langar (floating gardens) is also associated with the Mughal period. The beauty of Dal Lake presents a wonderful blend of Mughal and Kashmiri architecture. - Place in Kashmiri life and culture :
Dal Lake is an integral part of Kashmiri life. People here Jhelum River And Dal Lake They live in villages around the area , where their main occupation is fisheries , agriculture , and Handicrafts Dal Lake has a special place in Kashmiri culture , and the Jhelum Boat And Shikaras ( traditional boats) are an important part of the Kashmiri lifestyle.
Tours and attractions
- Shikaras : Famous of
Dal Lake Shikaras ( traditional Kashmiri boats) are a major attraction for tourists. Tourists board these Shikaras and travel in the calm and beautiful waters of the lake and during this time they enjoy the natural beauty of Kashmir. - Floating Market :
One in Dal Lake Floating Market It is a market where locals sell their products such as fresh fruits , flowers , shawls , and other handicrafts and textiles. This market is a unique experience in itself and is quite popular among tourists. - Mughal Garden :
Located on the banks of Dal Lake Nishat Bagh , Shalimar Bagh , and chashm-e-shahi Like Mughal gardens are a center of attraction for tourists. These gardens were built by the Mughal emperors to enhance the natural beauty of Kashmir. - Lotus flowers and vegetation in
Dal Lake Lotus flowers And Vegetation Lotus flowers are found in abundance. These natural scenes make the lake even more attractive. In the summer season, lotus flowers bloom on the surface here , which further enhance the beauty of the lake.
Economic and environmental aspects
- Tourism and employment :
Dal Lake is an integral part of Kashmir’s tourism industry. This area is not only attracting tourists but also providing employment to the people. Locals It is also a major source of employment for the people. Shikara rides , hotels-resorts , handicrafts and traditional boatman work provide employment to many people here. - Ecology and Environmental Threats :
Dal Lake is environmentally sensitive and has many environmental problems. Issues such as water pollution , haphazard construction and falling water level are affecting the ecology of the lake. Many plans are underway to address these problems , but it requires collective effort. - Water Pollution and Cleaning Drives :
Water pollution has become a serious problem in the lake. Domestic waste , sewage , and other pollutants get dumped into the lake , affecting its water quality. To tackle this problem, the government and various organizations are conducting cleaning drives and taking measures to improve the water quality.
Conclusion
Jammu and Kashmir is a unique state known for its natural beauty , rich cultural heritage , and historical importance. However , the politics and administrative changes here have kept it in the news. This region of India is moving towards development and peace.
want to know in depth about any particular topic like history , tourism , or culture , please let us know.
The geographical structure of Jammu and Kashmir makes it rich in natural beauty and environmental diversity. The height of the Himalayas , the greenery of the valleys , and the gurgling flow of the rivers make it unique. This region is not only a center of attraction for tourists but is also an important example of the geographical diversity of India.
The Kashmir Valley is unique due to its natural beauty and rich cultural heritage. It is a center of attraction for tourists not only from India but all over the world. Its unique geographical structure , vibrant traditions , and serene atmosphere make it a “heaven on earth”.
is unique for its religiosity , cultural diversity and natural beauty. It is considered a special place not only for pilgrims but also for history lovers and nature lovers. Jammu, the “city of temples” , is a confluence of spirituality and tradition.
Ladakh is an important part of India due to its natural beauty , cultural heritage , and unique geography. It is considered a center of adventure activities and spirituality. Ladakh is a center of attraction for tourists not only from India but also from all over the world .
The history of Ladakh reflects its cultural diversity and strategic importance. From an administrative point of view, Ladakh getting the status of a Union Territory has increased the possibilities of development. However , keeping in mind the geographical and border challenges , the administration needs to act with caution and sensitivity.
Jammu and Kashmir is an important part of India due to its natural beauty , cultural heritage , and strategic importance. The geographical and social challenges here can be a hindrance to development , but the efforts of the central and local administration are creating new possibilities of peace and progress in the region.
Article 370 and 35A was an important step in Indian history. It attempted to bring Jammu and Kashmir into the mainstream of development. However , it was also a controversial step , which created political
, social and security challenges. In the future , government efforts and the cooperation of the local people will help ensure peace and development in the region. will play an important role.
Ladakh is a unique and strategically important region of India. Its natural beauty , cultural heritage , and strategic importance give it a distinct identity. Despite the challenges , the region is achieving new dimensions of development and prosperity due to the efforts of the government and the local community.
The culture of Ladakh is a beautiful blend of its Buddhism , Tibetan traditions , and Islamic influences. Its art , literature , religion , and social traditions are famous all over the world. The region is a symbol of religious tolerance , cultural diversity, and rich cultural heritage.
Ladakh is a unique and attractive tourist destination , where tourists get a unique blend of adventure activities , cultural experiences , and natural beauty. This place is an ideal destination not only for the followers of Buddhism but also for adventure sports enthusiasts and nature lovers. Tourism in Ladakh definitely provides an unforgettable experience.
The Kashmir Valley is a region rich in historical and cultural heritage , renowned for its natural beauty , diverse culture , and rich history. Despite this , the economy and society face a number of challenges , including security issues , political instability , and environmental change. Nevertheless , the Kashmir Valley continues to grow and rebuild , and the region remains an important destination for tourists in India and around the world.
Jammu is a historically , culturally and religiously important region. The economic activities here are mainly based on agriculture , tourism , and handicrafts. Religious tourism , especially Vaishno Devi Yatra is the main identity of this region. Although there are some challenges in security situation and development , Jammu is still one of the major places of India due to its cultural and religious richness.
Dal Lake It is a major tourist destination and cultural heritage of Kashmir. It not only symbolizes the natural beauty of Kashmir but is also an important part of the history , culture and lifestyle of Kashmir . Along with this , continuous efforts are required to preserve and protect it from environmental point of view. If it is preserved properly, this region can become a sustainable and prosperous source of income for tourists and locals.
Ladakh’s economy is based on natural resources and government services. Tourism , agriculture , animal husbandry , handicrafts , and government services are the major income sources of the region. Although Ladakh’s economy faces limited resources and geographical challenges , it is growing rapidly , especially in the tourism and renewable energy sectors.
Jammu and Kashmir not only showcases the exquisite beauty of Kashmir but also holds immense historical, cultural, and lifestyle significance. To ensure its preservation and safeguarding from an environmental standpoint, continuous efforts are essential. Proper preservation can transform this region into a sustainable and prosperous hub for both tourists and locals, offering a diverse range of income sources including tourism, agriculture, animal husbandry, handicrafts, and government services. Despite facing limited resources and geographical obstacles, Ladakh’s economy is experiencing rapid growth, particularly in the tourism and renewable energy sectors.
