Detailed introduction of Maharashtra
Maharashtra It is a major state of India , known for its rich cultural heritage , historical importance and industrial progress. This state is located in the western part of India and is the second largest state of the country in terms of area and population.
1. Geographical location
- Capital : Mumbai
- Area : 3,07,713 square kilometers
- Geographical Range :
- In the north : Madhya Pradesh
- To the east : Chhattisgarh
- In the south : Karnataka and Goa
- To the west : Arabian Sea
- the North – West : Gujarat and Dadra & Nagar Haveli
2. History
The history of Maharashtra is very ancient. It was considered a part of ” Deccan ” in ancient times. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, founder of the Maratha Empire made this land great. The Maratha Empire played an important role in Indian politics in the 17th and 18th centuries. Apart from this, Maharashtra was also a leader in the freedom struggle.
3. Culture and tradition
The culture of Maharashtra is a fusion of diversity and colourful traditions.
- Language : Marathi is the main language of the state.
- Folk Dances : Traditional dances and games like Lavani , Koli , Tamasha and Dahi – Handi are famous.
- Festivals : Ganesh Chaturthi , Gokulashtami , Diwali and Holi are celebrated here with great enthusiasm.
- Food : Dishes like Vada Pav , Puran Poli , Misal Pav and Pav Bhaji are world famous.
4. Major cities and landmarks
- Mumbai : The economic capital of India and the hub of Bollywood.
- Pune : Educational and Cultural City.
- Nagpur : The city of oranges and centre of political importance.
- Aurangabad : Famous for Ajanta – Ellora caves and Bibi Ka Maqbara.
- Kolhapur : Famous for the Mahalaxmi Temple and Kolhapuri slippers.
5. Tourist Spots
Maharashtra has many historical and natural sites :
- Caves of Ajanta and Ellora ( UNESCO World Heritage Site ) .
- Gateway of India ( Mumbai ) .
- Mahabaleshwar and Panchgani ( hill station ) .
- Lonavala and Khandala ( natural beauty ) .
- Shivneri Fort ( birthplace of Shivaji Maharaj ) .
6. Financial condition
Maharashtra is the state with the largest economy in India.
- Main industries : films , information technology , automobiles , and manufacturing.
- Agricultural products : Sugarcane , cotton , rice , and grapes.
- Feature : Bombay Stock Exchange located in Mumbai and the Reserve Bank of India Make it financially stronger.
7. Natural resources
Maharashtra has abundant deposits of coal , iron ore , bauxite and limestone. Apart from this , rivers like Godavari , Krishna and Bhima are the main source of agriculture and water resources of the state.
8. Education and science
Pune is called the ” Oxford of the East ” . The state has several prestigious academic and research institutions :
- IIT Bombay
- Tata Institute of Fundamental Research
- Fergusson College ( Pune )
9. Current Scenario
Industrial and urban development is happening rapidly in Maharashtra. The state is a pioneer in metro services , smart city projects and cleanliness campaigns.
conclusion
is an important state of India due to its glorious history , diverse traditions and economic development. This state is a wonderful amalgamation of ancient and modern India.
Geographical location of Maharashtra

Maharashtra is located in the western part of India and is known for its geographical diversity and natural beauty. The geography of the state makes it ideal for agriculture , industry and tourism.
1. Status and extent
- Location in the country : Located in the western region of India.
- Latitude and Longitude :
- Latitude : 15° 40′ N to 22° 00′ N.
- Longitude : 72° 36′ East to 80° 54′ East.
- Limitations :
- In the North : Madhya Pradesh .
- the North – West : Gujarat and Dadra and Nagar Haveli .
- To the east : Chhattisgarh .
- In the south : Karnataka and Goa .
- To the west : Arabian Sea .
2. Area and structure
- Total area : 3,07,713 square kilometers.
- Location in India : Maharashtra is the third largest state in India in terms of area.
- Western Ghats : The western part of Maharashtra is surrounded by the Sahyadri mountain range ( Western Ghats ) . This region is famous for lush green forests and hill stations .
3. Geographical diversity
The geographical structure of Maharashtra can be divided into three main parts :
( a ) Plateau region
- Most of Maharashtra is the Deccan Plateau.
- The area is composed of volcanic rocks and is rich in black soil ( regur soil ) .
- Cotton and sugarcane cultivation is prominent here.
( b ) Sahyadri Mountains ( Western Ghats )
- It is located on the western side of the state.
- Coastal plains and high hills form the main part of this region.
- Mahabaleshwar , Lonavala and Khandala are located here.
( c ) Coastal area ( Konkan belt )
- It is spread along the coast of the Arabian Sea.
- This area is full of rivers , sea beaches and greenery.
- Ratnagiri , Sindhudurg and Raigad fall in this region.
4. Rivers
Many major rivers flow through Maharashtra , which are the mainstay of the state’s agriculture and water resources.
- Godavari River : Known as the ” Dakshina Ganga ” , it is the longest river in the state.
- Krishna River : Important river of South Maharashtra.
- Bhima River : Main water source for Pune and Solapur districts.
- Tapti and Narmada : Flow in the northern part of the state.
5. Climate
There are three main types of climate found in Maharashtra :
- Tropical Monsoon Climate : This climate is found in most parts of the state.
- Western Ghats Region : This region receives heavy rainfall.
- Plateau region : There is less rainfall and dry season.
6. Flora and Fauna
- Various types of forests are found in Maharashtra , among which the dense forests of the Western Ghats are prominent.
- Important National Parks :
- Tadoba – Andhari Tiger Reserve ( Chandrapur ) .
- Sanjay Gandhi National Park ( Mumbai ) .
- Navegaon National Park.
conclusion
The geography of Maharashtra plays an important role in the economic and cultural diversity of the state. The Sahyadri hills , the coastal areas of Konkan and the Deccan plateau make it geographically rich and environmentally diverse.
History of Maharashtra
The history of Maharashtra is very ancient , glorious and rich. This state has played an important role in the politics , culture , and economy of the Indian subcontinent from ancient times to the modern era.
1. Ancient times
The history of Maharashtra is linked to the Vedic period. It is called ” Great Nation ” or ” Maharashtra ” , which is mentioned in ancient literature and records.
( a ) Vedic and Puranic age
- Maharashtra was a major centre of Aryan culture during the Vedic period.
- Ramayana and the Mahabharata Like indirect mention of Maharashtra is found in the epics.
- Nashik and penetration Such places were major centres of religious and cultural activities.
( b ) Influence of Buddhism and Jainism
- Buddhism had a special influence in Maharashtra.
- Ajanta and Ellora Caves There are wonderful examples of Buddhist art and architecture.
- The influence of Jainism was also seen here , especially in Western Maharashtra.
2. Early dynasties ( Satavahana dynasty )
- The Satavahana dynasty ( 230 BC to 220 AD ) was the first major ruling dynasty of Maharashtra.
- This dynasty was famous for its patronage of trade and Buddhism.
- The Satavahanas developed Maharashtra as a prosperous trading centre.
- Prominent ruler : Gautamiputra Satakarni .
3. Medieval history
( a ) Rashtrakuta dynasty
- The Rashtrakuta dynasty (6th – 10th century ) took architecture and culture in Maharashtra to new heights.
- Their capital was Manyakheta ( in present-day Karnataka ) .
- The Rashtrakutas contributed significantly in the construction of the Ellora Caves.
- Famous King : Amoghavarsha I.
( b ) Yadav dynasty
- The Yadava dynasty (12th – 14th century ) gave Maharashtra an independent identity.
- Their capital was Devagiri ( present-day Daulatabad ) .
- Marathi language and literature flourished during the reign of the Yadava dynasty.
- Major ruler : Singhan Yadav .
4. Rise of the Maratha Empire
( a ) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj (1630–1680) was the founder of the Maratha Empire and a great hero in the history of Maharashtra.
- He established Swaraj and fought against the Mughals , Adilshahis and Nizamshahis.
- Shivaji built forts and established the Maratha navy.
- Major forts : Raigad , Sinhagad , Pratapgad.
- Shivaji Maharaj was awarded the title of Chhatrapati in Raigad in 1674 .
( b ) Peshwa rule
- The expansion of the Maratha Empire after Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was done by the Peshwas It happened under the leadership of.
- Peshwa Bajirao I expanded the empire from South India to North India.
- Capital : Pune.
- Third Battle of Panipat in 1761 It was an important event for the Maratha Empire.
5. British period
- Third Anglo – Maratha War in 1818 After this the Maratha Empire ended and Maharashtra came under British rule.
- Mumbai became a major commercial and administrative centre of British India.
- Maharashtra was a leader in the freedom struggle.
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak : Prominent leader of the freedom movement.
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar : Social reformer and architect of the Indian Constitution .
6. Maharashtra after Independence
- After independence , the state of Maharashtra was formed on 1 May 1960 .
- It separated from Gujarat and became an independent state.
- Mumbai was declared the capital of the state.
7. Culture and contribution
The history of Maharashtra has enriched the culture , language and art of India.
- Language : The literary and cultural development of Marathi language took place during the Yadava dynasty and the Maratha Empire.
- Religion : The influence of Buddhist , Jain , Hindu and Sufi traditions can be seen in every corner of the state.
- Arts : Maharashtra has been a centre of architecture , sculpture , and folk arts.
conclusion
The history of Maharashtra is a symbol of valour , cultural richness and self-reliance. This state will always be remembered for the Swaraj of Shivaji Maharaj , the military might of the Peshwas and its contribution to the freedom struggle.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj

Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was a great warrior of India , an efficient administrator and the founder of the Maratha Empire. His life is a symbol of valor , freedom , and justice. Shivaji Maharaj not only laid the foundation of a strong empire but also kept the spirit of Swaraj and Dharmaraksha alive in Indian history.
Early Life
- Born : 19 February 1630, Shivneri Fort , Pune.
- Father : Shahaji Bhosale ( a feudal lord under the Mughals and Adilshahis ) .
- Mother : Jijabai ( religious and virtuous woman ) .
- Guru : Saint Ramdas Swami.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s childhood was spent under the care of his mother Jijabai and Dadoji Konddev.
- were taught warfare skills , horse riding , and the strategic importance of forts.
Military and political achievements
1. Establishment of Swaraj
Shivaji Maharaj’s biggest goal was to establish Swaraj ( independent rule ) . With his skillful leadership and courage, he challenged the power of the Mughals , Adilshahis and Nizamshahis.
2. Forts strategy
- built and rebuilt about 300 forts to defend his empire .
- Major forts :
- Raigarh ( their capital ) .
- Pratapgarh.
- Sinhagarh.
- Lohgarh.
3. Guerrilla warfare ( ganimi kava )
- Shivaji Maharaj adopted guerrilla warfare techniques.
- The strategy was to attack the enemy suddenly and then retreat immediately.
- He used it effectively against the Mughals and the Adilshahis.
4. Establishment of a modern navy
- Shivaji Maharaj created an organised navy for the first time in the Indian subcontinent.
- His fleet protected the west coast from foreign invaders and pirates.
- Important ports : Sindhudurg , Vijaydurg.
Important Wars and Agreements
1. Killing of Afzal Khan (1659)
- Shivaji Maharaj treacherously defeated the Adilshahi commander Afzal Khan at Pratapgarh fort.
- This was a major victory for the Maratha Empire.
2. Plunder of Surat (1664)
- Shivaji Maharaj attacked Surat, hitting the economic backbone of the Mughals.
- This plunder helped in increasing their military and economic strength.
3. Treaty of Purandar (1665)
- Shivaji Maharaj made this treaty with Mughal commander Raja Jai Singh.
- Under this treaty he handed over some forts to the Mughals.
4. Conflict with Aurangzeb
- Shivaji fought bravely against the huge army of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb.
- In 1666 , Shivaji was treacherously imprisoned in the Agra Fort , but he cleverly managed to escape from there.
Coronation and expansion of the Maratha Empire
- Coronation : On 6 June 1674 , a grand coronation of Shivaji Maharaj took place at Raigad Fort.
- He assumed the title of ” Chhatrapati ” and established an independent Maratha Empire.
- Shivaji Maharaj developed a system of governance based on religion , justice and equality.
administrative law
Shivaji Maharaj was not only a skilled warrior but also an ideal administrator.
- Ashtapradhan Mandal : Shivaji formed a council of eight ministers to run his administrative system smoothly.
- Peshwa ( Prime Minister ) .
- Senapati ( Army Chief ) .
- judge.
- Law and Order : Shivaji improved tax collection and the judicial system.
- Religious Tolerance : He respected all religions and maintained religious tolerance under his rule.
Death
- Death : 3 April 1680, Raigad Fort.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s death was a major blow to the Maratha Empire , but his successors carried forward his legacy.
Legacy of Shivaji Maharaj
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj is not only a king but also a symbol of India’s freedom struggle and self-respect.
- Swaraj , religion and equality that he awakened in his time continues to inspire Indian society even today.
- Shivaji Maharaj is remembered with respect and reverence in Maharashtra and throughout India.
conclusion
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj not only laid the foundation of the Maratha Empire , but also created a unique history with his courage and administrative efficiency. He is an immortal personality in the history of India , who dreamt of Swaraj and made it a reality.
Culture and Tradition of Maharashtra

Maharashtra is one of the most culturally and traditionally rich states of India. Its culture is deeply influenced by history , religion , art , music , dance , food and folk traditions. The cultural heritage of Maharashtra reflects its diversity and unity.
1. Language and Literature
( a ) Marathi language
- Marathi is the Official language of Maharashtra.
- It is one of the major languages of India and developed since the 13th century.
- Sant Tukaram , Dnyaneshwar and Namdev enriched the Marathi language and literature.
( b ) Literature
- The literature of Maharashtra is influenced by devotional and social reform movements.
- Dnyaneshwari written by Saint Dnyaneshwar And the Abhangas of Sant Tukaram are major texts of Marathi literature.
- , the contribution of writers like Kusumagraj and V.S. Khandekar is significant.
2. Religious traditions
( a ) Worship of Lord Vitthal
- ( Vitath of Pandharpur ) is very popular in Maharashtra .
- Pandharpur Wari Yatra , in which thousands of devotees walk on foot to have darshan of Lord Vitthal , is the most important religious tradition of the state.
( B ) Saint Tradition
- Sant Tukaram , Sant Dnyaneshwar , Sant Eknath , and Sant Namdev inspired the Bhakti movement and social reform in society.
- These saints raised their voice against casteism and social inequality.
( c ) Ganeshotsav
- Ganesh Chaturthi is the biggest and most beautiful festival of Maharashtra Is.
- The festival is celebrated for 10 days and the idols of Lord Ganesha are immersed with a grand procession.
( d ) Diwali , Holi and Gudi Padwa
- Gudi Padwa It is the New Year of Maharashtra , which is celebrated on the first date of Chaitra month.
- Diwali There is a tradition of lighting Akashkandil ( chandelier of lamps ) .
3. Art and folk music
( a ) Dance and music
- Lavani : Traditional folk dance of Maharashtra , performed with fast pace and catchy songs.
- Koli Dance : This dance of fishermen reflects their lifestyle and life connected to the sea.
- Bhavageet : This Marathi song style is full of heart touching emotions.
( B ) Spectacle
- Tamasha is a traditional theatre form of Maharashtra , combining dance , music and storytelling.
- It reflects ancient folk traditions and is popular in rural areas.
4. Food
Maharashtra food is known for its hot , spicy and delicious dishes.
- Spicy dishes : Vada Pav , Misal Pav , Pav Bhaji.
- Traditional dishes : Puran Poli , Thecha , Thalipeeth.
- Sweets : Shrikhand , Puran Poli , Modak ( Lord Ganesha’s favourite ) .
- The food of Kolhapur , Pune and Konkan region has a special taste and variety.
5. Clothing Tradition
- Saree : The traditional Maharashtrian sari , called the Nauvari sari , is worn by women of Maharashtra.
- Men’s attire : Dhoti , kurta and turban.
- It is customary to wear traditional dress on festivals and special occasions.
6. Festival
( a ) Ganesh Chaturthi
- This is the biggest festival of Maharashtra.
- People install idols of Lord Ganesha in homes and pandals.
( b ) Gudi Padwa
- Maharashtra’s New Year , in which Gudi ( flag ) is hoisted.
- It is considered a symbol of prosperity and happiness in homes.
( c ) Narali Purnima
- This festival is especially celebrated by fishermen.
- Coconut is offered after worshipping the sea.
7. Traditional Games
- , Kabaddi and Lezim are the main traditional games of Maharashtra .
- Mallakhamb is a gymnastic art which is still popular today .
8. Social and cultural events
( a ) Pandharpur Wari
- It is a devotional journey of Sant Tukaram and Sant Dnyaneshwar , in which lakhs of people participate.
( b ) Marathi Sahitya Sammelan
- This is an annual event in which Marathi literature , language and culture are promoted .
9. Architecture and Crafts
( a ) Caves
- Ajanta and Ellora Caves : Amazing examples of Buddhist art and craft.
- Kanheri Caves and the Elephanta Caves .
( b ) Forts
- Forts in Maharashtra , such as Raigad , Sinhagad , and Pratapgad , reflect the might and architecture of the Maratha Empire.
10. Agriculture and rural life
- Rural life of Maharashtra is based on agriculture.
- Folk culture and traditions are deeply rooted in the villages.
- Rural festivals , such as Pola and bullock races , are part of the agricultural culture.
conclusion
The culture and tradition of Maharashtra reflects its rich and diverse cultural heritage. Its languages , festivals , food , art and religion all together give it a unique identity. The traditions of Maharashtra not only strengthen its cultural roots but also enrich its modernity.
Major cities and places in Maharashtra

many places and cities of historical , religious and cultural importance located in the state of Maharashtra. These places not only showcase the cultural diversity of the state but also symbolize the natural beauty and modernity of this place.
1. Mumbai
( a ) Characteristics
- Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra and is famous as the economic capital of India.
- is the centre of Bollywood ( the Indian film industry ) .
- Mumbai is India’s largest and busiest port.
( b ) Main site
- Gateway of India : A historical monument built during the British rule.
- Marine Drive : It is called the ” Queen ‘s Necklace ” .
- Haji Ali Dargah : A religious place situated in the middle of the sea.
- Siddhivinayak Temple : Famous temple of Lord Ganesha.
- Elephanta Caves : UNESCO World Heritage Site , famous for Shaivite sculptures.
- Juhu Beach : Mumbai’s most famous beach.
2. Pune
( a ) Characteristics
- Pune is called the ” cultural capital ” of Maharashtra.
- This city was a major centre of the Maratha Empire.
- Pune is also famous as an education and IT hub.
( b ) Main site
- Shaniwarwada Fort : Historical fort from the Peshwa era.
- Aga Khan Palace : An important site of the freedom struggle.
- Parvati Hill Temple : A beautiful religious and tourist place.
- Osho Ashram : Famous for meditation and yoga.
- Raja Dinkar Kelkar Museum : Museum of antiquities.
3. Nagpur
( a ) Characteristics
- Nagpur is called the ” Orange City ” because it is famous for orange cultivation.
- It is considered the geographical centre of India.
( b ) Main site
- Deekshabhoomi : The place where Dr. B. R. Ambedkar accepted Buddhism.
- Seminary Hills : Beautiful natural view of Nagpur.
- Ramtek Temple : Historical temple of Lord Rama.
- Ambazari Lake : A beautiful natural lake.
4. Aurangabad
( a ) Characteristics
- Aurangabad is called the ” Tourist Gateway of Maharashtra ” .
- It is famous for Ajanta and Ellora caves.
( b ) Main site
- Ajanta Caves : Amazing example of Buddhist art and architecture.
- Ellora Caves : Mixed sculpture of Hindu , Buddhist and Jain religions.
- Bibi Ka Maqbara : It is called the ” Taj Mahal of the Deccan ” .
- Daulatabad Fort : A historically and strategically important fort.
5. Nashik
( a ) Characteristics
- Nashik is called the ” Wine Capital of India ” .
- It is a city of religious importance and is located on the banks of the Godavari River.
( b ) Main site
- Trimbakeshwar Temple : One of the 12 Jyotirlingas.
- Panchvati : Historical site of Ramayana period.
- Sula Vineyards : India’s major wine producing region.
- Kumbh Mela Site : Kumbh Mela is organised here every 12 years.
6. Kolhapur
( a ) Characteristics
- Kolhapur is famous for its traditional Kolhapuri chappals and cuisine.
- It has religious and historical importance.
( b ) Main site
- Mahalakshmi Temple : Ancient temple of Goddess Mahalakshmi.
- Panhala Fort : A witness to the history of the Maratha Empire.
- Rankala Lake : A natural and beautiful lake.
7. Shirdi
( a ) Characteristics
- Shirdi is the land of Sai Baba and is a pilgrimage site for millions of devotees.
( b ) Main site
- Sai Baba Temple : The main temple of Sai Baba.
- Dwarkamai : An important place associated with the life of Sai Baba.
- Chavadi : Resting place of Sai Baba.
8. Solapur
( a ) Characteristics
- Solapur is famous for its cotton textile industry and bed sheets.
( b ) Main site
- Siddheshwar Temple : Ancient temple of Lord Shiva.
- Solapur Fort : Fort of historical importance.
- Akkalkot Swamy Maharaj Temple : A famous religious place.
9. Ratnagiri
( a ) Characteristics
- Ratnagiri is located in the Konkan region and is famous for its natural beauty and Hapus mango ( Alphonso ) .
( b ) Main site
- Ratnadurga Fort : A historical fort situated on the seashore.
- Thibaw Palace : Residence of the King of Burma.
- Ganapatipule : Famous temple of Lord Ganesha and beach.
10. Lonavala and Khandala
( a ) Characteristics
- These hill stations are famous for their lush green mountains, waterfalls and peaceful atmosphere .
( b ) Main site
- Bhushi Dam : A picnic spot.
- Lonavala Lake : Beautiful and serene lake.
- Rajmachi Fort : Ideal for trekking and history buffs.
11. Mahabaleshwar
( a ) Characteristics
- This hill station is famous for its cool climate and strawberry cultivation.
( b ) Main site
- Famous View Points : Arthur’s Seat , Wilson’s Point.
- Mahadev Temple : Ancient temple of Lord Shiva.
12. Tadoba – Andhari Tiger Reserve ( Chandrapur )
- It is the oldest and famous Tiger Reserve of Maharashtra.
- Here tigers and other wildlife can be seen in their natural habitat.
conclusion
The major cities and sites of Maharashtra symbolize its cultural diversity , historical heritage , religious significance and natural beauty. These sites make the state one of the most prosperous and tourist – loving regions of India.
Major tourist places in Maharashtra

Maharashtra is a state of India which is famous for its historical , religious , natural and cultural heritage . The tourist places here attract tourists due to their diversity and uniqueness. Let us know in detail about the major tourist places of Maharashtra :
1. Ajanta and Ellora Caves ( Aurangabad )
( a ) Ajanta Caves
- These are Buddhist caves , which are included in the UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The paintings and sculptures here belong to the Mahayana and Hinayana branches of Buddhism.
- These caves depict events related to the life of Lord Buddha.
( b ) Ellora Caves
- These caves belong to Hindu , Buddhist and Jain religions.
- Kailash Temple ( Cave No. 16) is the main attraction of Ellora.
- It is the largest single stone structure in the world.
2. Gateway of India ( Mumbai )
- It is a major tourist destination of Mumbai , built in 1924 during the British rule.
- It is situated on the seashore and is an attractive place for tourists.
- Nearby are the Taj Mahal Palace Hotel and the Elephanta Caves.
3. Ganpatipule ( Ratnagiri )
- It has a famous temple of lord Ganesha and a beach.
- This place is known for its natural beauty and peaceful environment.
- The Ganesha temple here is situated on a hill , and the idol is naturally formed.
4. Mahabaleshwar and Panchgani
( a ) Mahabaleshwar
- It is a famous hill station , famous for its cool climate and strawberries.
- Major places : Arthur’s Seat , Wilson Point , Venna Lake.
( b ) Panchgani
- Located near Mahabaleshwar, this hill station is known for its beautiful valleys and environment.
- The views of sunset and sunrise from here are amazing.
5. Lonavala and Khandala
- These hill stations are located in the Sahyadri ranges and are famous for their natural beauty.
- Major attractions : Bhushi Dam , Lonavala Lake , Tiger Leap.
- This place becomes even more beautiful during the rainy season.
6. Raigad Fort
- This was the main fort of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Raigad was the capital of the Maratha Empire.
- Trekking and ropeway options are available to reach here.
7. Marine Drive ( Mumbai )
- It is called the ” Queen ‘s Necklace ” because the lights make it shine like a necklace at night.
- It is a major tourist destination , where people come to stroll on the seashore and enjoy the sunset.
8. Tadoba – Andhari Tiger Reserve ( Chandrapur )
- It is the oldest and famous tiger reserve of Maharashtra.
- Along with tigers, other wildlife like leopard , deer , bear and various species of birds can be seen here.
- This place attracts tourists for safari.
9. Shirdi
- Shirdi is the pilgrimage place of Sai Baba.
- The Sai Baba temple here attracts millions of devotees every year.
- Major places : Dwarkamai , Chavadi , Gurudwara.
10. Alibaug ( Konkan Coast )
- It is a beautiful seaside town , called ” Mini Goa ” .
- The beaches here , like Alibaug Beach and Nandagaon Beach , are popular among tourists.
- Alibaug’s fort and coconut plantations are also an attraction.
11. Kolhapur
- This is a religious and historical place.
- Major places : Mahalaxmi Temple , Panhala Fort , Rankala Lake.
- Kolhapur is also famous for its traditional chappals and spicy cuisine.
12. Pune
- Pune is the cultural capital of Maharashtra.
- Major places : Shaniwar Wada , Aga Khan Palace , Osho Ashram.
- , museums and historical places here attract tourists.
13. Ajantha Caves ( Aurangabad )
- Ajantha Caves reflect the grandeur of Buddhism.
- The paintings and sculptures here are excellent examples of ancient Indian art.
14. Maval ( Pawana Lake and Fort )
- Pawna Lake is a beautiful and serene lake , ideal for picnics.
- The nearby Lohagad Fort and Visapur Fort are famous for trekking.
15. Nashik
- This is a religious and historical place.
- Major places : Trimbakeshwar Jyotirlinga , Panchvati , Sula Vineyards.
- Kumbh Mela is also organised here.
16. Bhimashankar
- This is the Jyotirlinga temple of Lord Shiva.
- is also famous for its lush green forests and natural beauty.
conclusion
Maharashtra is known for its variety of tourist destinations. It is full of historical, religious , natural and cultural places. These places not only reflect the rich heritage of the state but also provide a wonderful experience to the tourists.
Ajanta and Ellora Caves
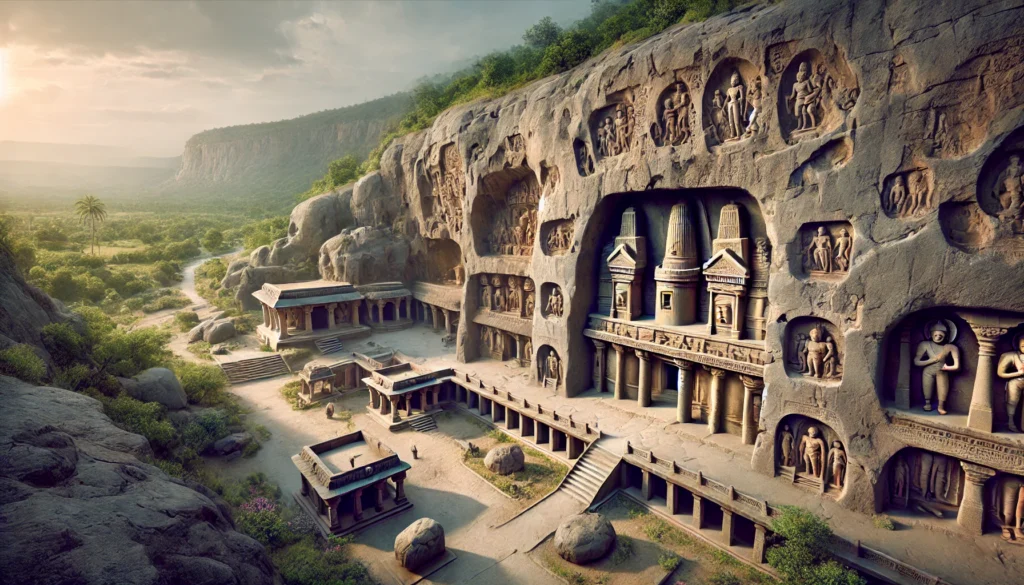

Ajanta and Ellora Caves These are ancient and historical caves of India , located in the state of Maharashtra. These caves are not only a part of India’s rich cultural heritage , but are also recognized by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites . A unique blend of art , architecture , and religious beliefs can be seen in these caves.
1. Ajanta Caves
Location : Ajanta Caves , Aurangabad district of Maharashtra which is located in Jalgaon These caves are about 100 kilometers away from the Vagora River . Are situated on the banks of.
History :
- Ajanta Caves were constructed over a period of 2 centuries – the first phase began in the 7th century and the second phase in the fifth century In.
- were intended as a place of meditation , worship , and mindfulness for Buddhist monks .
features :
- Paintings and Architecture : Ajanta Caves are famous for their amazing wall paintings and wood crafts These caves depict depictions related to Buddhism , such as events from the life of Buddha , Lord Bodhisattva , and various Buddhist stories. Are prominent.
- Caves : Ajanta has a total of 30 caves , which include meditation centres ( viharas ), worship places ( chaityas ), and galleries decorated with paintings.
- Major Caves : Cave 1 ( Chaitya ), Cave 2 ( paintings of Buddha’s life ), Cave 17 ( amazing paintings ), and Cave 26 ( Buddha statue ) are the major caves.
Art and Painting :
The paintings of Ajanta caves depict the main themes of Buddhism. These include the philosophy of God , the teachings of Buddha , and the paintings depicting the meditation of Buddhist monks. The style of light colours and detailed visualization in the paintings has given a special identity to these caves.
2. Ellora Caves
Location : Ellora Caves are also located in Aurangabad district , which is about 100 kilometers away from Ajanta Caves. These caves are located in Ellora village It is located near , and from here the Kailash Temple Is also quite famous.
History :
- The Ellora Caves were constructed between the 5th century and the 10th century.
- These caves house a combination of temples and art from Buddhism , Jainism and Hinduism , reflecting the diversity of the site.
features :
- Music and Crafts : The Ellora Caves are famous for their huge and intricate architecture These caves are famous for a magnificent Kailash temple . It is a 100-metre-high (1.6 ft) deep cave , which has been carved out of a single rock. It is a unique example of art.
- Caves : There are a total of 34 caves in Ellora , out of which 12 caves are related to Buddhism , 17 caves to Hinduism and 5 caves to Jainism.
- Major caves : Cave 1 ( Buddhist chaitya ), Cave 10 ( vihara ), Cave 16 ( Kailash temple ), Cave 21 ( Vishnu images ), and Cave 32 ( related to Jainism ) are the major ones.
- Kailash Temple : This temple is the only temple in the world which is built by hollowing out a single rock. This temple is famous for its architecture all over the world.
Art and Painting :
The Ellora caves are a blend of the art of Buddhism , Hinduism and Jainism. Kailash Temple The grand and detailed craft work has made it a major attraction. The paintings here depict Lord Shiva , Vishnu , Buddha , and various other gods and goddesses.
Importance of Ajanta and Ellora Caves
- Cultural Heritage : These caves are a unique heritage of Indian art , religion , and culture.
- World Heritage Site : Both the caves are declared as World Heritage Site by UNESCO. are recognised as such.
- Spiritual and Religious Outlook : Buddhist , Hindu and Jain religions are represented in these caves , symbolising Indian secularism and religious tolerance.
conclusion
The caves of Ajanta and Ellora are not only masterpieces of Indian architecture and art , but also present a unique blend of religious and cultural heritage. Visiting these caves is not only a historical journey , but also an opportunity to understand the deeper meanings of Indian culture and religious beliefs.
Economic condition of Maharashtra
Maharashtra is one of the most prosperous states of India and contributes significantly to the country’s economy. It has a balanced mix of agriculture , industry , service sector and trade , which makes it economically strong.
1. Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP)
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Maharashtra It is highest in India.
- This state contributes about 15% to the country’s GSDP. contributes to.
- Maharashtra’s annual GSDP is around US$ 400 billion has more than , making it one of the most economically developed states in India.
2. Agricultural sector
- Agriculture is a major occupation in Maharashtra.
- The main crops grown here are:
- Kharif Crops : Rice , Millet , Sorghum , Maize.
- Rabi crops : Wheat , gram.
- Cash Crops : Cotton , Sugarcane , Soybean , Groundnut.
- , banana , orange , and mango are also cultivated here on a large scale.
- Vidarbha and Marathwada regions are prominent for agriculture.
- The use of drip irrigation and advanced agricultural techniques is increasing rapidly in the state.
3. Industrial area
- Maharashtra is the largest industrial state of India.
- Major Industries :
- Automobile : Pune , Aurangabad and Nashik are centres of automobile manufacturing.
- Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals : There are numerous industrial plants near Thane and Mumbai.
- Cotton Textile Industry : Mumbai was formerly called the ” City of Mills ” .
- Micro , Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) : Millions of people are associated with small and medium industries.
- MIDC (Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation) Various industrial areas have been developed by.
4. Service sector
- The service sector is a major part of Maharashtra’s economy.
- Key Services :
- Finance and Banking : Mumbai is the financial capital of India , where the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE) Are located.
- Information Technology (IT) : Pune , Mumbai and Navi Mumbai have developed as IT hubs.
- Tourism : Tourism plays a major role in the state. Places like Ajantha – Ellora , Shirdi , Lonavala attract a large number of tourists.
5. Trade and investment
- Mumbai is the business and commercial centre of the country.
- is the most preferred state for foreign investment (FDI) .
- The headquarters of many multinational companies and financial institutions are located here.
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT) It is the largest container port in the country.
6. Employment and Labour Force
- Agriculture , industry and service sectors provide employment to millions of people in Maharashtra.
- Urban areas : Employment opportunities are more in cities like Mumbai , Pune , Navi Mumbai.
- Rural areas : Employment mainly based on agriculture and cottage industries.
- The state government has promoted self-employment and women empowerment through various schemes.
7. Contribution of tourism
- Maharashtra is full of religious , natural and historical tourist places.
- Major places : Mumbai , Ajanta – Ellora , Shirdi , Mahabaleshwar , Lonavala , Raigad.
- The state government has made a special policy to promote tourism.
8. Infrastructure
- Maharashtra has the most developed infrastructure in India.
- Roads : National Highways and Mumbai – Pune Expressway.
- Railways : Mumbai has the largest network of Indian Railways and offers suburban rail services.
- Airports : Mumbai and Pune are the major international airports.
- Port : Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT) is India’s largest container port.
9. Financial and Banking Hub
- Mumbai is the financial centre of India.
- The country’s largest banks , insurance companies and stock markets are located here.
- The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE) are the major financial institutions here.
10. Major Challenges
- Agricultural crisis : Many farmers in Maharashtra are affected by drought and falling crop prices.
- Pressure of Urbanisation : Pressure on infrastructure due to population growth in cities like Mumbai and Pune.
- Unemployment and migration : Migration from rural to urban areas.
conclusion
Maharashtra is the centre of India’s economic development. Its diversified economy , which includes agriculture , industry and service sectors , makes it one of the most important states in the country. Government policies and schemes will help make Maharashtra even more prosperous.
Natural Resources of Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a rich state of India , which is full of various types of natural resources. This state is known for its mineral wealth , forest resources , water resources and agricultural land. The natural resources here play an important role in the economic and social development of the state.
1. Mineral resources
Mineral wealth is available in abundance in Maharashtra. Many types of minerals are found here , which are used in various industries.
( a ) Major minerals
- Coal :
- High quality coal is found in Chandrapur and Nagpur areas.
- This mineral contributes to the state’s energy production.
- Iron Ore :
- Gadchiroli has deposits of iron ore.
- This mineral is important for the steel industry.
- Manganese :
- There are manganese deposits in Bhandara and Nagpur region.
- Bauxite :
- Bauxite is found in Kolhapur and Satara , which is used in aluminium production.
- Limestone :
- This mineral, important for the cement industry, is found in various districts.
- Dolomite and Silica :
- These minerals are useful in glass and other industries.
2. Water resources
( a ) Rivers
Many important rivers flow through Maharashtra , which contribute to irrigation , drinking water and energy production.
- Godavari River : It is also called ” Dakshin Ganga ” .
- Krishna River : It originates from the Western Ghats and is important for agriculture.
- Bhima , Tapi , Pench , and Wardha Rivers : Helpful in irrigation and water supply of the state.
( b ) Dams and reservoirs
- Koyna Dam :
- The largest dam in Maharashtra.
- It is important for hydroelectric power generation and irrigation.
- Ujani Dam : Located on Bhima River.
- Jayakwadi Dam : It is situated on the Godavari River.
- Water management is done through these dams.
3. Forest resources
Maharashtra has a large area of forests , which contribute to wildlife conservation , climate balance and natural beauty.
( a ) Forest area
- 20% of the land area of Maharashtra It is covered with forests.
- Major forest areas :
- Sahyadri Mountain Range .
- Vidarbha region .
- , Teak , Bamboo , Mahua and Tendu are found in the forests here .
( b ) Wildlife
- The state has Tadoba – Andhari Tiger Reserve , Melan Ghat Sanctuary , and Navegaon National Park Such as are major wildlife areas.
- Tiger , leopard , deer , and many bird species are found here.
4. Agricultural land and soil
( a ) Types of soil
- Maharashtra has diverse soil types , which are suitable for agricultural production.
- black soil :
- Found in Vidarbha and Marathwada region.
- Famous for cotton cultivation.
- Red Soil :
- It is found in Konkan region.
- Useful for paddy and sugarcane cultivation.
- Sandy and rocky soil :
- In the Sahyadri mountain range.
- black soil :
- These soils help in growing a variety of crops in the state.
( b ) Agricultural products
- A large part of agriculture in Maharashtra is dependent on rain.
- Cotton , soybean , sorghum , millet , sugarcane are grown here and paddy are the major crops.
- The state produces horticultural products such as grapes , oranges , and bananas He is also leading in .
5. Energy resources
( a ) Hydroelectricity
- Maharashtra has many hydroelectric projects , such as the Koyna Hydroelectric Project.
- A large part of the state is dependent on hydropower.
( b ) Thermal power plant
- There are thermal power plants at Chandrapur and Parli.
- Coal is used in production of electricity.
( c ) Wind and solar energy
- There are wind power projects in Satara and Sangli.
- The state is also making rapid progress in solar energy production.
6. Marine and coastal resources
- Maharashtra has a 720 km long coastline It is rich in natural resources.
- Fishing and salt production are the main activities here.
- Alibaug , Ratnagiri , Sindhudurg For example, coastal areas are famous for marine biodiversity.
7. Natural resources related to tourism
- Natural beauty and hill stations in Maharashtra like Mahabaleshwar , Lonavala , Khandala and Matheran attract tourists.
- Trekking and jungle safari can be enjoyed in the Sahyadri mountain range.
conclusion
Maharashtra is one of the richest states in India due to the diversity of its natural resources. These resources play an important role in the state’s economy , environmental balance , and livelihood of the people. Long-term use of these resources can be ensured through proper management and conservation.
Education and science in Maharashtra
Maharashtra is one of the leading states in India in the field of education and science. The state is famous for high quality education , research institutions and scientific progress. The state has made significant contributions to social and economic development through education and science.
1. Education system
( a ) School education
- Many initiatives have been taken to improve primary and secondary education in Maharashtra.
- Government and private schools Working throughout the state.
- To make education universal, the state government has launched Saraswati Yojana and free textbook schemes Have started.
- Medium : Here education is given in Marathi , Hindi and English medium.
( b ) Higher education
- Maharashtra has many prestigious universities and colleges for higher education.
- Major Universities :
- Mumbai University
- Pune University (Savitribai Phule Pune University)
- Nagpur University
- Marathwada University
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University
( c ) Technical and vocational education
- IIT Bombay : It is one of the top technical institutes in India.
- VIT (VIT Pune ) and COEP Pune Such institutes are famous for technical education.
- polytechnic colleges in maharashtra and ITI (Industrial Training Institutes) The network of is also strong.
( d ) Education reform programme
- Mid – Day Meal Scheme : To increase the attendance of children in school.
- E – learning : Spreading digital education in rural areas.
- Women’s Education : Special schemes to promote girls’ education.
2. Science and research
There has also been great progress in the field of science and research in Maharashtra.
( a ) Scientific institute
- Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Mumbai
- It is famous for research in fields like physics , mathematics and biology.
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), Mumbai
- It is India’s major centre of nuclear energy and research.
- National Chemical Laboratory (NCL), Pune
- It is famous for chemistry and industrial research.
- CSIR Centres
- Scientists contribute in the field of research.
( b ) Technical research
- Artificial Intelligence , Data Science , and Robotics in Maharashtra Like many centers are working for modern technological research.
- Pune and Mumbai are leaders in IT and software research.
3. Medical and health education
( a ) Medical education
- KEM Hospital , Mumbai and BJ Medical College , Pune Such institutions are famous for medical education.
- , Homeopathy and Unani medicine are also taught here .
( b ) Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals
- Biotechnology in Pune and Mumbai and pharmaceuticals Research is carried out in the area of.
- The National Institute of Virology (NIV) in Pune plays a vital role.
4. Innovation and startup culture
- Maharashtra , especially Mumbai and Pune , is emerging as a hub for startups in India.
- The state government has launched the Maharashtra Startup Policy has started.
- IT Hub : Pune and Navi Mumbai have established Information Technology (IT) There has been unprecedented progress in the field of.
- Fintech and e – commerce Innovations are being promoted in the region.
5. Contribution to science and technology
( a ) Nuclear energy
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) and Tarapur Atomic Power Plant are located in Maharashtra.
- It is the main centre for nuclear power production in India.
( b ) Space research
- Maharashtra Scientist ISRO contribute to various campaigns of the.
( c ) Green Energy
- Research and development is being carried out in Maharashtra in the field of solar and wind energy.
6. Spread of rural education and science
- International Rural University for the promotion of education and science in rural areas And various non – governmental organizations (NGOs) are working.
- Anna Hazare and his village Ralegan Siddhi Presented the ideal of rural development using environment and science.
7. State Government Initiatives
- Gyanarjan Abhiyaan : To provide quality education to the children.
- Digital India Mission Promotion of e – learning in Maharashtra under .
- Mission Shakti : To increase the participation of women in science and technical education.
conclusion
Maharashtra has established its leading position in the field of education and science. The presence of higher education institutions and research centres in the state encourages scientific thinking and the development of modern technologies. By combining education and science , Maharashtra has made an unprecedented contribution to social and economic development.
Current Scenario of Maharashtra
Maharashtra is currently emerging as a rapidly changing and developing state. This state is not only a major part of India’s economy , but its social , political , and cultural status is also constantly changing.
1. Political scenario
The political scenario of Maharashtra has also changed a lot in the last few years.
( a ) The present government
- Mahavikas Aghadi (MVA) The alliance , comprising Shiv Sena , Congress and NCP , was running the government in Maharashtra , but recently there was a major change in politics after the split of Shiv Sena.
- Shiv Sena ( Uddhav Thackeray faction ) and Shiv Sena ( Eknath Shinde faction ) Eknath Shinde after the dispute between the two took over as Chief Minister and B.J.P. formed an alliance with.
- There remains stability and change of power in politics in the state , which can affect the pace of development.
( b ) Elections and voting
- Assembly elections in Maharashtra are held every 5 years.
- 2024 will also impact the political scenario of the state.
- Election issues generally relate to development , unemployment , agrarian crisis , and secularism.
2. Economic scenario
The economy of Maharashtra is diversified and the state is contributing significantly to the economic development of the country.
( a ) GSDP of the state
- GSDP of Maharashtra It is one of the largest states in India and contributes around 15% to India’s total GSDP.
- Major industries in Maharashtra include automobiles , agriculture , pharmaceuticals , information technology (IT) , and the service sector Are included.
- Cities like Pune and Mumbai are gearing up for the IT sector are the major centres of , while Nagpur , Nashik , and Aurangabad Such cities are contributing significantly to industrial development.
( b ) Agricultural crisis
- Many regions of Maharashtra , such as Marathwada and Vidarbha , severe drought and agricultural crisis are facing.
- The government has made many schemes to solve the agricultural crisis , like loan waiver scheme and drought relief package .
- Agricultural Productivity New technological measures and irrigation projects are being implemented to increase it.
( c ) New industrial policy
- Maharashtra government has announced new industrial policy has implemented the scheme , which aims to attract domestic and foreign investment To attract.
- The state government has announced the Startup Policy has also been promoted so that new entrepreneurs can get support .
3. Social scenario
Maharashtra is a culturally and socially diverse state , home to communities of different religions , castes and languages.
( a ) Education and health
- Education : Continuous work is being done towards improving the education system in the state. Maharashtra Education Department e – learning and online education has been boosted , especially after Covid -19 .
- Health : Pandemic (COVID-19) After , the state government has implemented several schemes to improve health services.
- Schemes for Vulnerable Groups : The government has launched schemes for women empowerment , education schemes for children , and special schemes for backward and scheduled castes / tribes. Have made it.
( b ) Women’s rights and gender equality
- Many schemes have been made for women empowerment in Maharashtra. The state government has set up a Women Commission has strengthened the Nari Suraksha schemes to prevent violence against women have been implemented.
- Many schemes are running to provide education , health and employment opportunities to women .
4. Environmental and climate crisis
The impacts of environmental and climate change are continually being felt in Maharashtra.
( a ) Lack of rainfall
- Drought in many parts of the state and water crisis The problem of water scarcity is increasing. Areas like Marathwada and Vidarbha are facing severe water scarcity due to lack of rainfall.
- The government has started promoting water recycling and rainwater harvesting have made plans for.
( b ) Natural disasters
- flood and dry Such natural calamities are common in the state.
- Alibag , Ratnagiri , and Sindhudurg As in coastal areas, beach related problems are increasing.
- Kolhapur , Sangli , and Nashik In areas like these, the problems of flood and waterlogging are emerging seriously.
5. Cultural and tourist scenario
Maharashtra is a major state for cultural heritage and tourists.
( a ) Religious tourism
- Shirdi ( Sai Baba Temple ), Pandharpur ( Vitoba Temple ), and Trimbakeshwar ( Shiva Temple ) attract millions of tourists.
- Ajanta and Ellora Caves They are famous as world heritage sites.
( b ) Cultural events
- Ganesh Utsav in Maharashtra And Diwali Like there are big festivals , which are celebrated with great pomp throughout the state.
- Pune And Mumbai There are many cultural programs of art , music and dance.
6. Challenges and Opportunities
( a ) Challenges
- Agrarian crisis , unemployment , and urbanization The problem of are the major challenges.
- environmental crisis , climate change and natural disasters are impacting the economy and lifestyle of the state.
( b ) Opportunity
- IT and service sector , tourism and renewable energy There are immense possibilities in this field in Maharashtra.
- Startups and innovation Promoting it can further improve the state’s economy.
conclusion
The current scenario of Maharashtra is a mixture of development and challenges. The state is moving towards prosperity through its diverse cultural , social and economic resources , but some difficulties are also coming up due to agricultural crisis , environmental problems and political changes. To deal with these challenges, plans and new direction of development are needed.
